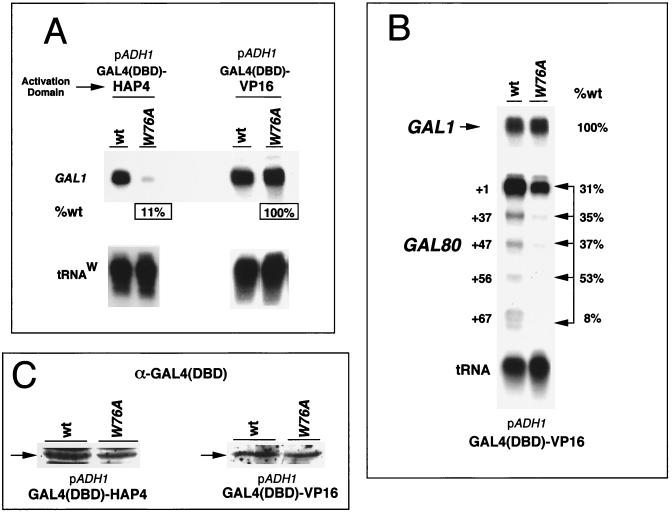
FIG. 7.
Activator- and promoter-specific defects of toa2 mutant alleles. (A) The GAL4-VP16 and GAL4-HAP4 activators were compared for their ability to activate the endogenous GAL1 promoter in wt or toa2 W76A strains. The activators were expressed by the ADH1 promoter under conditions of glucose repression. RNA levels were determined by S1 analysis and quantitated by PhosphorImager. Percentage of wt activity is indicated for the W76A mutant-derived mRNA. DBD, DNA binding domain. (B) The endogenous GAL1 and GAL80 promoters were compared for activation by the GAL4-VP16 activator in the wt and toa2 W76A strains. RNA levels were assayed by S1 analysis, and PhosphorImager quantitation is presented as the percentage of wt levels. Multiple TR start sites are indicated for GAL80. TR induction by GAL4-VP16 in SC medium with 2% glucose was compared for the wt and toa2 Y69A strains. The percentage of wt transcription for each GAL80 start site is indicated. Experiments were performed at least twice in duplicate, and the error was less than 15% (data not shown). (C) Western blot analysis of GAL4-VP16 and GAL4-HAP4 expression levels in the wt and toa2 W76A strains. Cell extracts were derived from cultures grown under identical conditions to those used for panels A and B. GAL4-VP16 and GAL4-HAP4 were expressed from the ADH1 promoter.