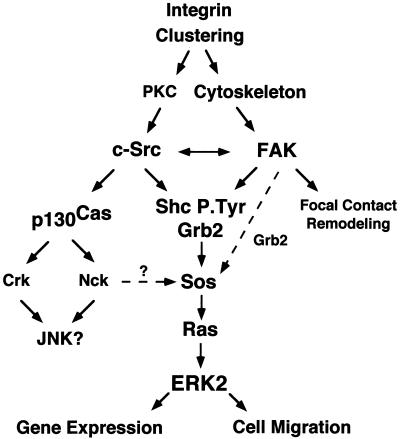
FIG. 10.
Model of the integrin signaling network to ERK2. FN stimulation of cells promotes integrin clustering and signals that can independently activate FAK or Src family PTKs. Integrin-stimulated c-Src activation may be downstream of PKC-mediated events, whereas integrin-stimulated FAK activation is dependent upon the integrity of the actin cytoskeleton. FAK and c-Src transiently associate and translocate to the Triton-insoluble fraction of cells after FN stimulation, and this association may mutually enhance and extend the time course of their integrin-stimulated PTK activity. Both FAK and c-Src can phosphorylate Shc at multiple sites to promote Grb2 adapter protein binding, whereas c-Src phosphorylation of FAK at Tyr-925 also promotes Grb2 binding. Grb2 SH3 domain association with the Sos GDP-GTP exchange protein can activate Ras, and ERK2/MAP kinase is one downstream target of Ras-mediated signaling events. It is proposed that maximal signaling to ERK2 would result from the stimulation of multiple pathways, whereas lower levels of integrin-stimulated signaling to ERK2 can occur in the absence of either Src family or FAK PTK activity. Integrin-stimulated c-Src PTK activity promotes p130Cas tyrosine phosphorylation and Crk and Nck adaptor protein binding to p130Cas, which may link integrins to the activation JNK or ERK2/MAP kinase pathways. Integrin-activated ERK2 may function to promote gene transcription by phosphorylation of targets in the nucleus or ERK2 may promote cell migration through phosphorylation and enhanced activation of myosin light-chain kinase (29). FAK may play multiple roles as a scaffold for the recruitment of signaling proteins and function in the processes of cell substratum remodeling events during cell spreading or migration.