Figure 1. CXCL4 recruits a wide range of different leukocytes in vivo.
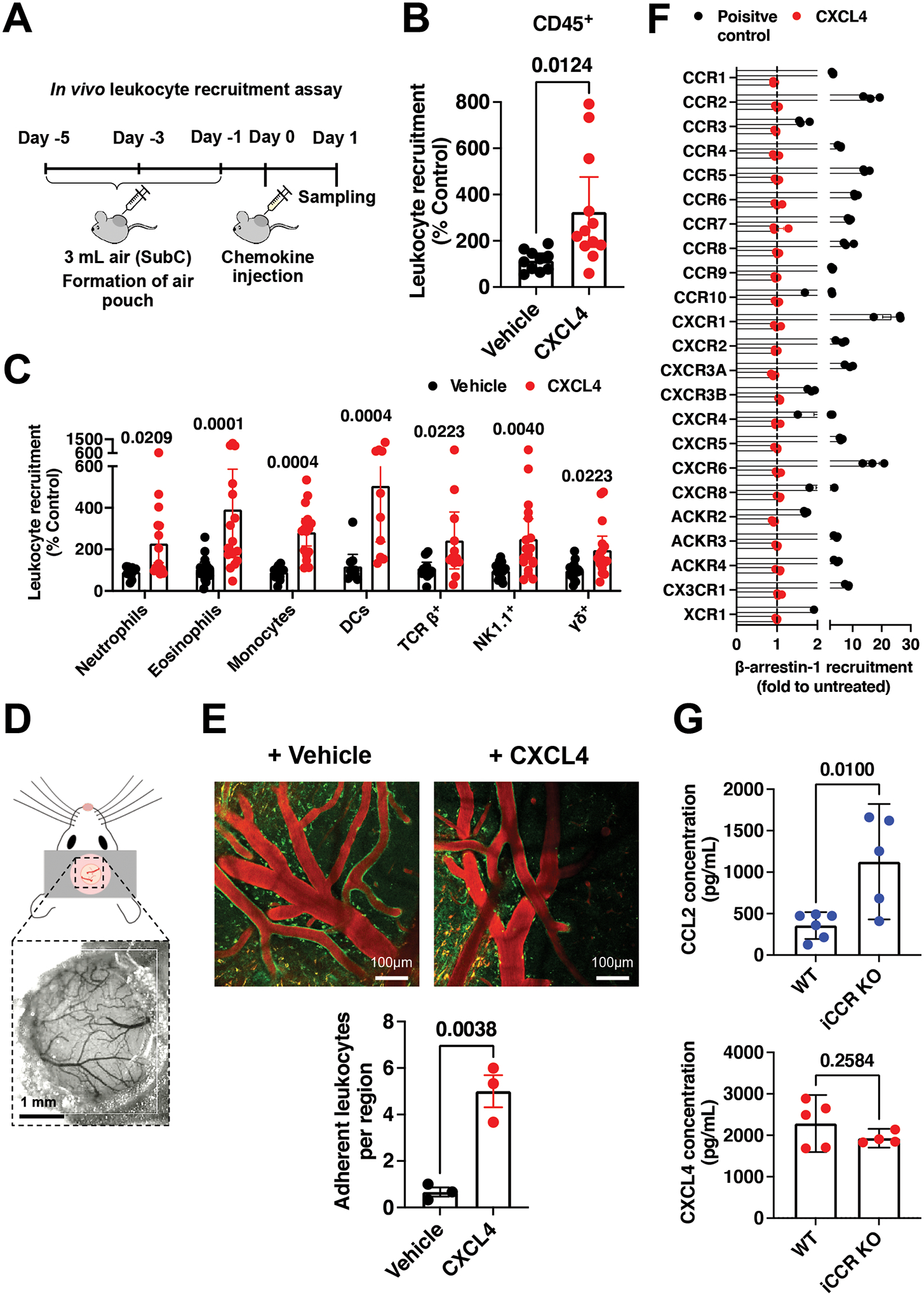
(A) Schematic of the in vivo leukocyte recruitment assay. (B) CD45+ cell counts 24 hr after CXCL4 injection. (C) Quantification of different leukocytes recruited by CXCL4. (D) Schematic of cranial window implantation for in vivo leukocyte adhesion analysis. (E) In vivo analysis of leukocyte (labelled green) adhesion to the walls of the vasculature (labelled red) following injection of CXCL4 or vehicle control. (F) Agonist activity of CXCL4 (100 nM) towards 19 classical and 3 atypical chemokine receptors evaluated in a β-arrestin-1 recruitment assay. For all receptors, one known agonist chemokine (100 nM) listed in the IUPHAR repository of chemokine receptor ligands was added as positive control. (G) CCL2 and CXCL4 quantification in the serum of wild type or iCCR (CCR1, 2, 3 and 5) KO inflamed mice.
All plots are mean with 95% confidence intervals and represent at least two separate experiments, data have been pooled and each dot in B, C, E and G represents an individual mouse and each dot in F represents the mean of an individual experiment. B and C are normalised to vehicle controls. Results in F are expressed as fold change relative to untreated controls and are presented as mean of three independent experiments. Individual p values are shown, B, E and G analysed using an unpaired t-test and C analysed using a one-way ANOVA with a post-hoc Sidak analysis of log-transformed data.
