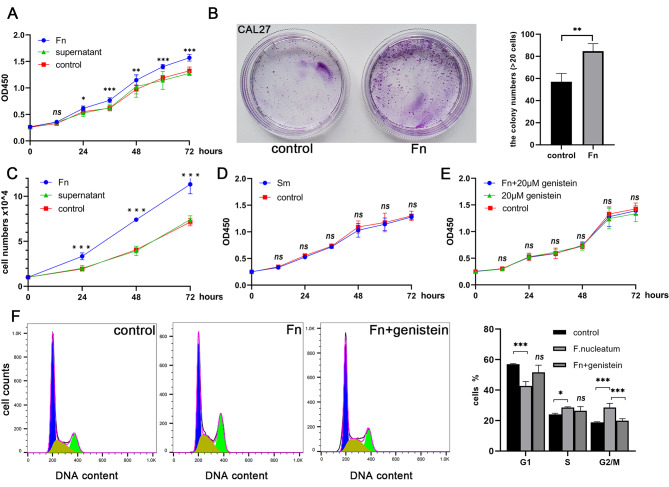
Fig. 1.
Methodological approach for studying cell proliferation in OSCC cells, with a focus on CAL27, conducted in three replicates. (A) Utilizing the CCK-8 assay, the influence of F. nucleatum and its supernatant on CAL27 cell proliferation was assessed. (B) Method to determine cell clone formation post-F. nucleatum intervention. (C) A 72-hour cocultivation followed by a cell counting procedure revealed an approximately 100% acceleration in cell growth, though the supernatant displayed negligible impact. (D) Control observation was employed to assess the proliferation effects of S. mutans on the cells, indicating no induction of cell proliferation. (E) Post-exposure effects of genistein on CAL27 cells in relation to (F) nucleatum was analyzed, highlighting genistein’s nullifying effects on F. nucleatum’s pro-proliferative attributes. F. A comparative cell cycle analysis encompassing the control, the F. nucleatum-treated, and the genistein-treated groups was performed, accompanied by statistical evaluations. (*, P<0.05; **, P<0.01; ***, P<0.001.)