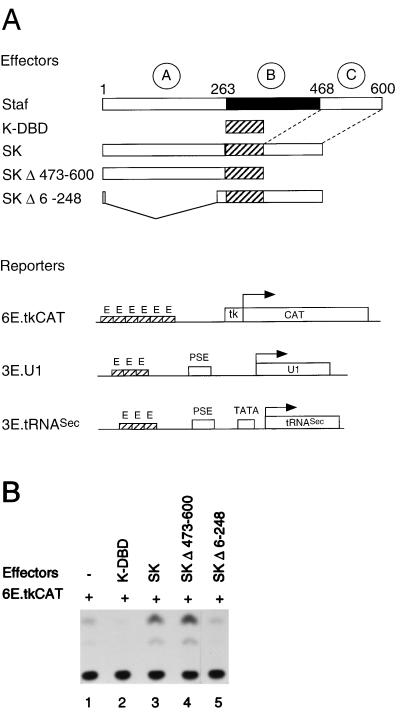
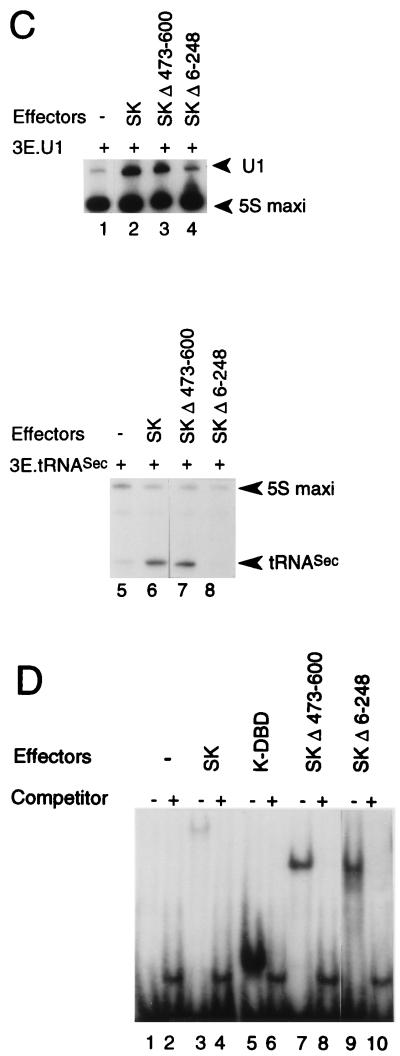
FIG. 1.
The Staf-Krox-20 chimera requires the N terminus to activate transcription from tk.CAT, U1 snRNA, and tRNASec promoters. (A) Schematic diagrams depicting the effector mRNAs synthesized in vitro and the 6E.tkCAT, 3E.U1 and 3E.tRNASec reporter genes used in the Xenopus microinjection assay. The first lane shows the structure of Staf. The A, B, and C domains are indicated with their localizations. PSE and TATA correspond to the basal promoter elements of the U1 and tRNASec genes. 3E and 6E indicate the number of multimerized E binding sites of the Krox-20 protein. SK, chimeric Staf-Krox-20 molecules. (B) CAT assays showing transcriptional activation from the 6E.tkCAT promoter by the K-DBD, SK, SKΔ473-600 and SKΔ6-248 effectors using extracts from microinjected Xenopus oocytes. Lane 1, no effector was expressed. (C) Transcriptional activation from the Pol II 3E.U1 (lanes 1 to 4) and Pol III 3E.tRNASec (lanes 5 to 8) promoters by the SK, SKΔ473-600 and SKΔ6-248 effectors using microinjected Xenopus oocytes. Lanes 1 and 5, no effector was expressed. Positions of the U1, tRNASec, and 5S maxi used as an internal standard are indicated. (D) Effector expression assayed by gel retardation with nuclear extracts from microinjected Xenopus oocytes. The identity of the expressed effector is indicated above each lane. Lanes 1 and 2, no effector was expressed. Reactions in lanes 1, 3, 5, 7, and 9 (−) contained no competitor; lanes 2, 4, 6, 8, and 10 (+) contained a 100-fold molar excess of unlabeled E competitor DNA.