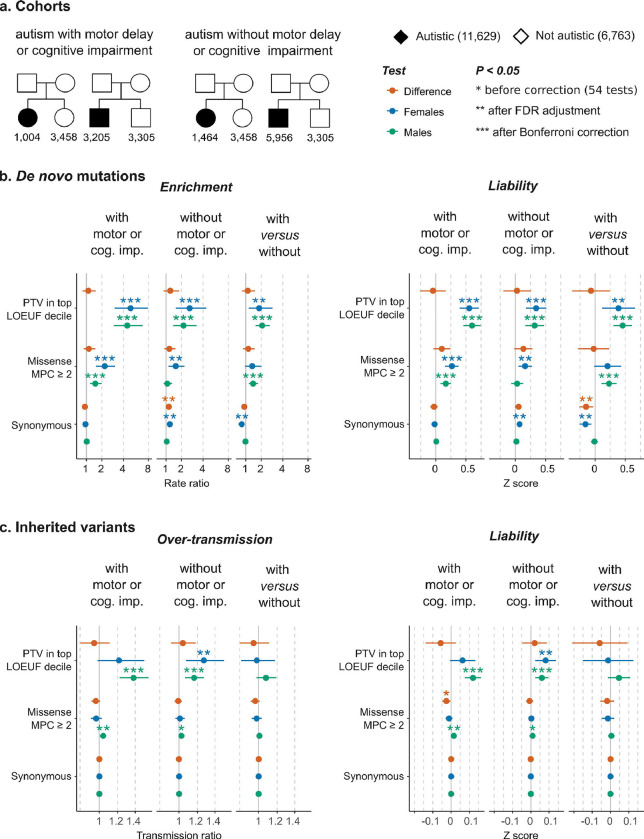
Figure 2:
Rare variant burden in autistic individuals with and without cognitive impairment or motor delay in SPARK trio-sequenced cohort. a, The sample size in two sub-cohorts of trio-sequenced individuals from the Simons Foundation Powering Autism Research for Knowledge study (SPARK) divided based on the presence of co-occurring motor developmental delays or cognitive impairment. b, Sex-stratified observed de novo mutation rates (left) and average liability (right) (see Methods). In addition to the comparisons versus siblings, autistic probands with motor or cognitive difficulties were compared directly to sex-matched autistic individuals without these co-occurring conditions (‘with versus without’). c, Over-transmission of rare inherited variants (left) and their average liability (right) (see Methods). The results depicted in this figure are available in Supplementary Table S6 (see the Extended Tables). See section 4.1.3 of the Supplementary Results (see the Supplementary Note) for details on the imbalance of synonymous variants. Limiting the analysis in b to ultra-rare DNMs in ancestry-matched autistic females and siblings showed well-balanced synonymous DNM burden (p = 0.42; Figure S13).