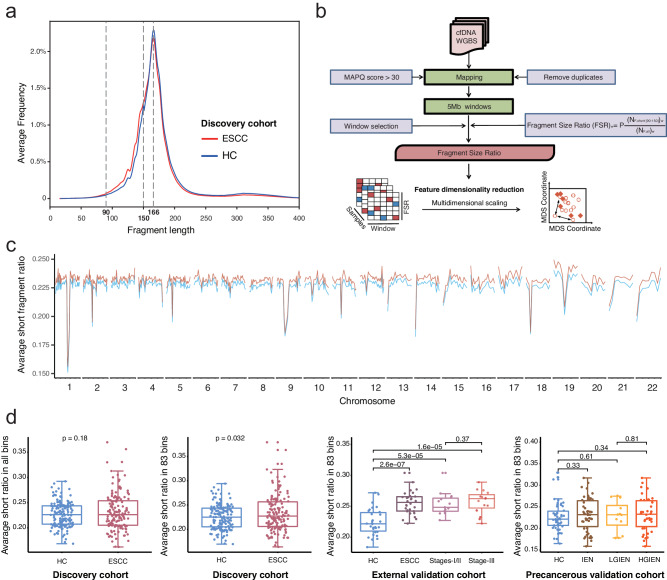
Fig. 4. Analyzing the cell-free DNA fragment size in whole-genome bisulfite sequencing data.
a The fragment sizes of cfDNA were surveyed in the discovery cohort. Both the peaks in cfDNA were 166 bp in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) patients and healthy controls. However, more short fragments (90–150 bp) were found in the ESCC groups. b The ratio of short fragments in cfDNA was calculated as the fragment size ratio (FSR) in whole-genome bisulfite sequencing data. c. The human genome was divided into 5 Mb bins, resulting in a total of 1082 (541 bins × 2) FSR features. d In the discovery cohort, no significant difference in the average FSR was observed across all bins between ESCC patients and HCs. However, we identified 83 bins where the FSRs were significantly elevated in ESCC patients than HCs in the discovery cohort. The average FSRs in the 83 selected bins were significantly higher in the ESCC patients in the discovery cohort and the external validation cohort, but not the intraepithelial neoplasia patients in the precancerous validation cohort (two-sided Mann–Whitney U-test, p < 0.05). Data are presented as median values with maximums and minimums. ESCC esophageal squamous cell carcinoma, IEN intraepithelial neoplasia, LGIEN low-grade IEN, HGIEN high-grade IEN, HC healthy control, WGS whole-genome sequencing, WGBS whole-genome bisulfite sequencing, MAPQ mapping quality, MDS multidimensional scaling. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.