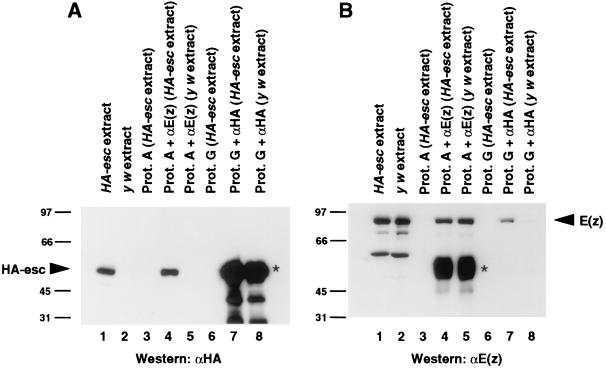
FIG. 2.
Coimmunoprecipitation of HA-esc and E(z) from Drosophila embryo extracts. Proteins were immunoprecipitated from embryo extracts with either anti-HA or anti-E(z) antibodies as indicated. Equal amounts of immunoprecipitates were separated on SDS gels, transferred to nitrocellulose filters, and incubated with anti-HA (A) or anti-E(z) (B) antibodies. Lanes: 1, 30 μg of extract from HA-esc embryos; 2, 30 μg of extract from y w embryos; 3, mock immunoprecipitation from HA-esc extract by protein (Prot.) A-Sepharose without antibody; 4, immunoprecipitation from HA-esc extract with anti-E(z) antibody; 5, immunoprecipitation from y w extract with anti-E(z) antibody; 6, mock immunoprecipitation from HA-esc extract by protein G-Sepharose without antibody; 7, immunoprecipitation from HA-esc extract with anti-HA antibody; 8, immunoprecipitation from y w extract with anti-HA antibody. Bands corresponding to HA-esc and E(z) are indicated by arrowheads. In panel B, lanes 1 and 2, the smaller species are E(z) degradation products. Signals indicated by asterisks in panel A, lanes 7 and 8, and panel B, lanes 4 and 5, are due to cross-reactivity between the secondary antibodies and the heavy chains of the antibodies used in immunoprecipitations. Numbers at left of panels are kilodaltons.