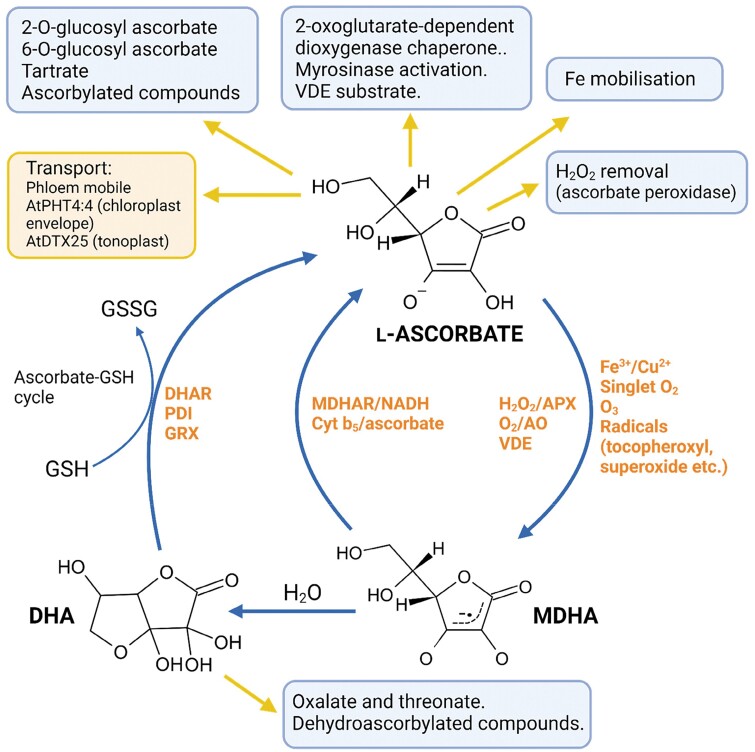
Fig. 1.
An overview of the chemistry and functions of ascorbate in plants. Ascorbic acid is predominantly present as the ascorbate anion (pKa1= 4.25). It acts as a reductant/antioxidant by reducing radicals and other reactive oxygen species by one electron transfer. H2O2 removal requires catalysis by plant-specific ascorbate peroxidases. It is unreactive with oxygen unless catalysed by ascorbate oxidase. Fe3+ and Cu2+ are readily reduced to Fe2+ and Cu+. MDHA, a resonance-stabilized radical, is the product of ascorbate oxidation. Ascorbate is an effective antioxidant because MDHA disproportionates to form DHA (most probably present as a bicyclic hemiketal form rather than the tricarbonyl structure commonly depicted) plus ascorbate. Otherwise it is reduced by MDHAR and by transmembrane reduction via cytochrome b5 which uses ascorbate as electron donor. DHA is reduced by thiols such as glutathione in the ascorbate–glutathione (Foyer–Halliwell–Asada) cycle. Ascorbate is phloem mobile and may be taken up via an unidentified plasma membrane DHA transporter, otherwise only chloroplast envelope and tonoplast ascorbate transporters have been identified. It is further metabolized to glucosides and breakdown products (in a species-dependent manner) while ascorbate and DHA can (dehydro)ascorbylate small molecules and proteins. As an antioxidant in plants, H2O2 removal using APX is the best studied function, while the physiological significance of its reactions with other radicals is less well characterized. Related to Fe, it is a protectant of the large 2-oxoglutarate-dependent dioxygen family and there is emerging evidence for a role in Fe nutrition. It is a substrate for VDE and, specifically for glucosinolate-producing species (such as Arabidopsis), it is involved in the catalytic site of myrosinases (Shikita et al., 1999) which release isothiocyanates from glucosinolates following herbivore damage. Created with BioRender.com. Abbreviations: AO, ascorbate oxidase; APX, ascorbate peroxidase; DHA, dehydroascorbate; DHAR, dehydroascorbate reductase; GRX, glutaredoxin; GSH, glutathione; GSSG, oxidized glutathione; MDHA, monodehydroascorbate radical; MDHAR, monodehydroascorbate reductase; PDI, protein disulfide isomerase; VDE, violaxanthin de-epoxidase.