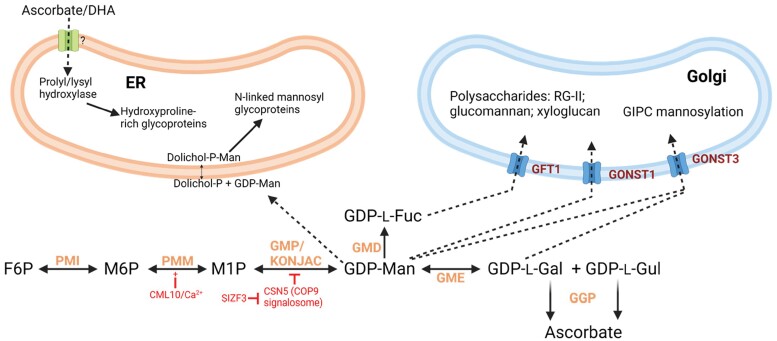
Fig. 3.
The dual role of GDP-sugars in glycosylation and ascorbate synthesis. The processing of glycoproteins destined for secretion (including structural proteins such as extensin and peptide hormones) occurs in the ER. Mannose is delivered to the ER via dolichol-P and used for protein N-glycoslyation. Additionally, the ER is the site of proline and lysine hydroxylation of glycoproteins by ascorbate-dependent 2-oxoglutarate-dependent dioxygenases (see Fig. 6). Glycan and glycosylinositol phosphoceramide synthesis in the Golgi uses GDP-sugars imported by various transporters. Considering the need to maintain a balance between the use of GDP-sugars for glycoproteins and polysaccharides required for cell wall production during growth and ascorbate synthesis, there is evidence that PMM is activated by interaction with a calmodulin-like protein (CML10) and GMP is subject to proteolytic breakdown by interaction with CSN5, which is antagonized by interaction of SIZF1 with CSN5. GMP is activated by two KONJAC proteins, which have a GMP-like sequence but no enzyme activity themselves. GDP-sugar availability will also be controlled by how much is used for ascorbate synthesis and, accordingly, GGP activity can act as a valve between ascorbate synthesis and glycoprotein/glycan synthesis. Created with BioRender.com. Abbreviations: DHA, dehydroascorbate; ER, endoplasmic reticulum; F6P, fructose 6-P; GDP-l-Fuc, GDP-l-fucose; GDP-l-Gal, GDP-l-galactose; GDP-l-Gul, GDP-l-gulose; GDP-Man, GDP-mannose; GIPC, glycosylinositol phosphoceramide; GMD, GDP-mannose-3,6-dehydratase=MUR1; GME, GDP-mannose-3',5'-epimerase; GMP, GDP-mannose pyrophosphorylase; GPP, l-galactose 1-P phosphatase; PMI, phosphomannose isomerase; M6P, mannose 6-P; M1P, mannose 1-P; PMM, phosphomannose mutase; RG-II, rhamnogalacturonan II.