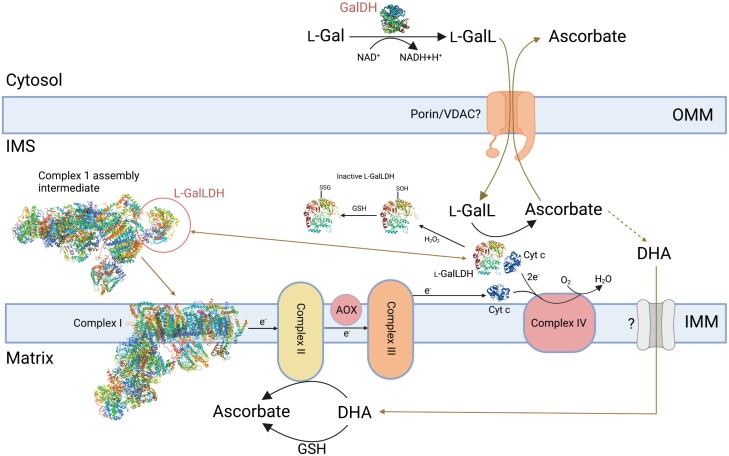
Fig. 5.
The final step of ascorbate synthesis is localized in mitochondria. l-GalL produced in the cytosol by l-GalDH enters the intermembrane space, presumably via carriers on the outer mitochondrial membrane (e.g. porins/VDACs). l-GalL is oxidized to produce ascorbate by l-GalLDH which transfers electrons to loosely associated Cyt c via an FAD cofactor. The reduced Cyt c transfers electrons to oxygen with production of water in Complex IV. Ascorbate leaves the mitochondrion, possibly thorough porin. Ascorbate enters the mitochondrial matrix as DHA. Mitochondria take up DHA in preference to ascorbate, but the IMM transporter is not identified. DHA is reduced in the matrix by GSH or by Complex II. GalLDH is oxidized by H2O2in vitro on a specific cysteine, resulting in an inactive sulfenic acid form which can be glutathionylated. GalLDH activity increases in the light, but it is not known if oxidation has a role in vivo. Remarkably, l-GalDH is also an essential component of Complex 1 assembly and is not present in the mature complex. The mitochondrial electron transport chain is not shown in detail. The Complex 1 cryo-EM and l-GalDH crystal structure are from the Protein Data Bank (https://www.rcsb.org) (accession nos 7A24, 7A23, and 7SMI). The l-GalLDH structure was predicted by AlphaFold (https://alphafold.ebi.ac.uk/). Created with BioRender.com. Abbreviations: AOX, alternative oxidase; DHA, dehydroascorbate; GSH, glutathione; IMM, inner mitochondrial membrane; IMS, intermembrane space; l-Gal(DH), l-galactose (dehydrogenase); l-GalL(DH), l-galactonolactone (dehydrogenase); OMM, outer mitochondrial membrane; VDAC, voltage-dependent anion channel.