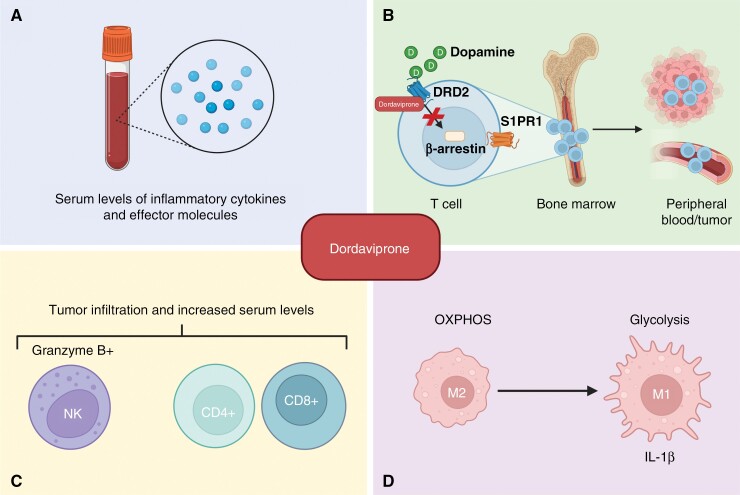
Figure 4.
Dordaviprone influences the immune microenvironment. (A) Dordaviprone increases levels of circulating inflammatory cytokines and effector molecules. (B) Proposed mechanism of dordaviprone-induced release of sequestered T cells in the bone marrow. Dordaviprone antagonizes DRD2 signaling, preventing β-arrestin from internalizing S1PR1. S1PR1 surface localization promotes T-cell trafficking. (C) Dordaviprone increases CD4+ and CD8+ T cell levels, as well as NK cells both in the peripheral blood and in the tumor microenvironment of solid tumors, (D) to reprogram macrophage metabolism driving the proinflammatory M1 phenotype.