Figure 5. Schematic diagram of the FTY720 (fingolimod) CNS mechanism of action (MOA) through B12 and IFN-β signaling.
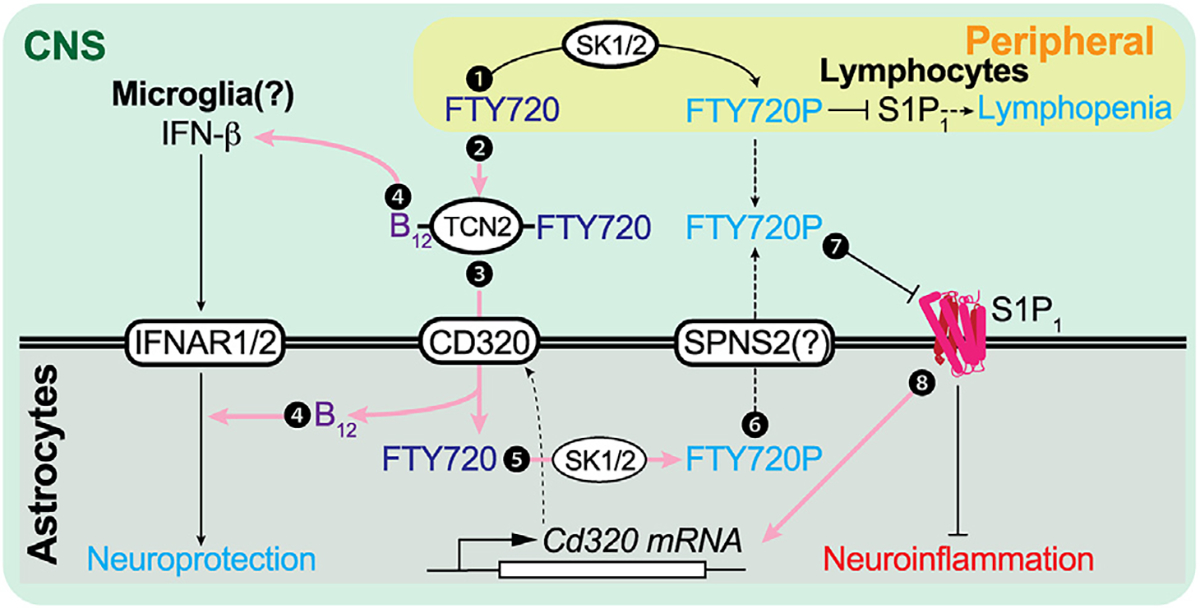
Pink arrows indicate newly identified pathways that contribute to the direct CNS effects of FTY720 beyond functional antagonism of astrocyte S1P1. ① S1P1 inhibition in peripheral lymphocytes is the originally proposed CNS MOA. ② FTY720 is complexed with B12-TCN2. ③ This FTY720-TCN2-B12 complex is taken up by astrocytes via CD320, followed by dissociation of the complex. ④ B12 is essential for astrocyte IFN-I sensitivity and microglial IFN-β production. ⑤ Astrocyte SK1/2 phosphorylates FTY720 to form FTY720P.35 ⑥ The resulting FTY720P may be transported via SPNS256 and functionally antagonizes S1P1 in an autocrine/paracrine manner. ⑦ FTY720P functionally antagonizes astrocyte S1P1 and downregulates cell surface expression of S1P1. Ⓑ Astrocytic S1P1 inhibition increases CD320 expression, enabling increased engagement of and astrocyte internalization of the B12-TCN2-FTY720 complex. SK1/2, sphingosine kinase 1/2; SPNS2, SPNS lysolipid transporter 2; TCN2, transcobalamin; IFNAR, interferon α/β receptor.
