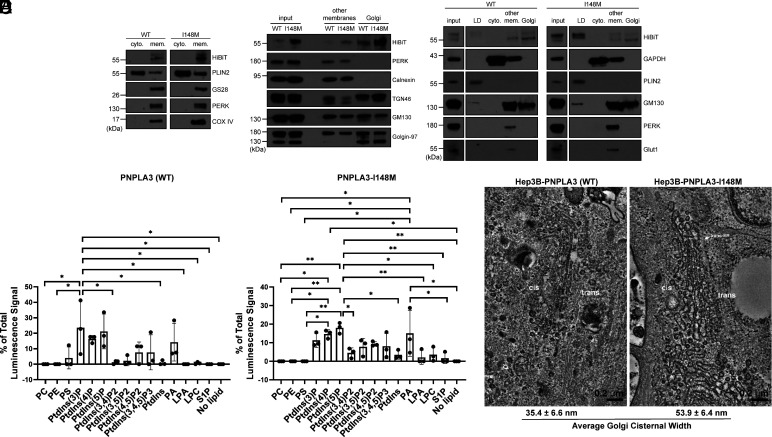
Fig. 2.
PNPLA3-I148M induces structural changes at the Golgi apparatus. (A) Basal-state Hep3B cells expressing endogenous PNPLA3-HiBiT or PNPLA3-I148M-HiBiT were fractionated into cytosolic (“cyto.”) or total membrane (“mem.”) fractions. (B) Basal-state Hep3B-HiBiT cells were further fractionated to separate membrane species. Other membranes include non-Golgi membranes. (C) Hep3B-HiBiT cells were treated with 100 µM oleic acid for 16 h prior to fractionation into LD, cytosolic, other membranes, and Golgi membrane fractions. (D) Purified PNPLA3-His and PNPLA3-I148M-His were incubated with phosphoinositide strips containing spots with 100 pmol of different lipid species. Following washing and staining with anti-His-HRP, strips were imaged using chemiluminescence. Bar graph represents the average of three independent experiments. P-values were calculated from an ordinary one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test. (E) Hep3B cells (WT or I148M) were treated with 100 µM oleic acid for 16 h, then fixed and imaged by TEM. Average cisternal widths were calculated from 20 Golgi cisternae per cell type. Fractionation studies (A–C) were repeated 2 to 4 times with similar results. TEM (E) was repeated twice. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01.