Table 4.
USP inhibitors involve in overcoming drug resistance of cancers
| Target | Inhibitor | Chemical structure | Enzyme activity/IC50 | Cancer type | Biological mechanism in drug resistance | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| USP7 | P22077 |
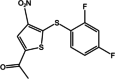
|
USP7/USP47 (8µM) |
Neuro-blastoma | P22077 enhances the cytotoxic effects of Dox and etoposide in NB cells with an intact USP7-HDM2-p53 axis. | [84] |
| HCC | P22077 induces cell death, inhibits cell proliferation and migration and decreases cell sensitivity to chemotherapy. | [82] | ||||
| Pancreatic cancer | P22077 reduces protein synthesis, and alters the extracellular space matrix to overcome Dox resistance. | [83] | ||||
| Acute myeloid leukemia | P22077 reduces cell proliferation, blocks DNA replication progression and increases the killing effect of cytarabine. | [254] | ||||
| Lung cancer | Combination treatment with the mitotic kinase PLK1 inhibitor volasertib and the P22077 shows a strong synergism through down-regulation of MDR1/ABCB1 in paclitaxel-resistant lung cancer. | [104] | ||||
| Chronic lymphocytic leukemia | P22077 eliminates leukemia stem/progenitor cells and overcomes imatinib resistance through destabilizing YB-1 and inhibiting DDR. | [154] | ||||
| P5091 |
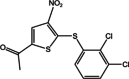
|
USP7(4.2µM) | Multiple myeloma | P5091 induces apoptosis in MM cells and overcomes BTZ resistance. Combining P5091 with lenalidomide, HDAC inhibitor SAHA, or dexamethasone triggers synergistic anti-MM activity. | [177] | |
| Multiple myeloma | P5091 and NEK2 inhibitor together overcome BTZ resistance through regulating NF-κB signaling pathway and the PP1α/AKT axis. | [175] | ||||
| Multiple myeloma | RRx-001 plus P5091 triggered synergistic anti-MM activity and overcome BTZ resistance. | [255] | ||||
| Lung neuro-endocrine tumor | P5091 sensitizes lung neuroendocrine tumor cells to PARP inhibitor by lowering CCDC6 and HR repair. | [147] | ||||
| Prostate cancer | P5091 accelerates the degradation of AR and CCDC6, sensitizing cancer cells to PARP-inhibitors. | [145] | ||||
| Lewis lung carcinoma | P5091 upregulates PD-L1, deregulates PD-1 and reprogramming TAMs in TME, enhancing the anti-tumor immune response. | [209] | ||||
| GNE6776 |
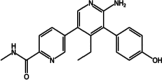
|
USP7(1.34µM) | TNBC | GNE-6776 increased apoptosis in chemoresistant TNBC cells through inhibiting the interaction between USP7 and ABCB1. | [93] | |
| HBX19818 |
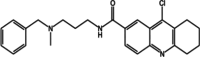
|
USP7(4.2µM) | Chronic lymphocytic leukemia | P22077 sensitizes p53-defective, chemoresistant CLL cells to chemotherapeutic agents through the accumulation of DNA damage. | [172] | |
| Compound41 |
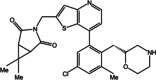
|
USP7(0.44nM) | NSCLC | Compound 41 resensitizes MYCN-overexpressing chemoresistant NSCLC cells to cisplatin and etoposide treatment by decreasing N-MYC protein and increasing apoptosis. | [256] | |
| USP1 | GW7647 |
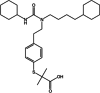
|
USP1/UAF1 (5µM) |
NSCLC | GW7647 in combination with cisplatin together enhances monoubiquitylation of PCNA and FANCD2 to promote therapeutic efficacy. | [40] |
| Pimozide |
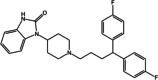
|
USP1/UAF1 (1.96µM) |
Lung cancer | The combination of pimozide and MAST1 inhibitor lestaurtinib sensitizes cells to cisplatin by reducing MAST1 expression and subsequent phosphorylation of MEK1 and ERK. | [43] | |
| B-cell lymphoma | Pimozide shows a synergetic effect with etoposide in rituximab/chemotherapy resistant cells through destabilization of MAX. | [257] | ||||
| SJB3-019A (SJB) |
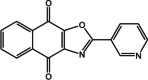
|
USP1/UAF1 (781nM) |
Multiple myeloma | Combining SJB with the ACY-1215, BTZ, lenalidomide, or pomalidomide shows synergistic cytotoxicity through activating apoptosis, inhibiting DNA repair and HR, as well as the downregulating stem cell renewal. | [258] | |
| ML323 |
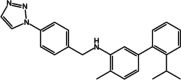
|
USP1/UAF1 (76nM) |
NSCLC | ML323 enhances the cytotoxicity of cisplatin in resistant NSCLC by inhibiting the deubiquitylation of PCNA and FANCD2. | [38] | |
| Breast cancer and ovarian cancer | ML323 kills BRCA1 deficient cells that have acquired resistance to PARP inhibitors due to replication fork stabilization. | [143] | ||||
| USP13 | Spautin-1 |
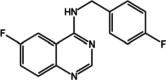
|
USP10/USP13, (0.6-0.7µM) | Ovarian cancer | Spautin-1 disrupts the formation of RAP80-BRCA1 complex foci and impairs DDR, thus rendering cancer cells sensitive to olaparib. | [137] |
| Gastro-intestinal stromal tumor | Spautin-1 induces the decay of ATG5 and co-administration of spautin-1 with 3-methyladenine enhances the therapeutic efficacy of imatinib. | [158] | ||||
| USP14 | b-AP15 |
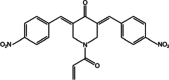
|
USP14/UCHL5 (2.1µM) |
Waldenström macro-globulinemia | b-AP15 can induce apoptosis in cells overexpressing Bcl-2 and lacking functional p53 to overcome BTZ resistance. | [259] |
| VLX1570 |
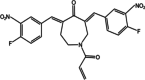
|
USP14/UCHL5 (10µM) |
Waldenström macro-globulinemia | VX1570 promotes rapid and tumor-specific apoptosis in WM cells resistant to BTZ or ibrutinib. | [173] | |
| IU-1 |
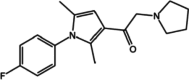
|
USP14(4.7µM) | Colorectal cancer | IU1 combined with anti-PD-1 enhances the anti-tumor response through regulating the infiltration ratio of CD8+ T cells and FOXP3+ Treg cells, also inhibiting IDO1-mediated immune suppression. | [228] | |
| USP8 | DUBs-IN-2 |
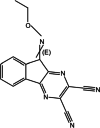
|
USP8(0.93µM) | - | DUBs-IN-2 leads to the upregulation of PD-L1, triggering immune responses and antigen presentation through TRAF6-NF-κB signaling pathway to enhance the efficacy of anti-PD-1/PD-L1 immunotherapy. | [207] |
| Pancreatic cancer | The combination therapy of DUBs-IN-2 and anti-PD-L1 suppress tumor growth, which is mediated by the activating anti-tumor immunity relies on the PD-L1 pathway and CD8+ T cells. | [206] | ||||
| 9-ethyloxyimino-9H-indeno[1,2-b] pyrazine-2,3-dicarbonitrile |
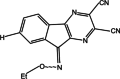
|
USP8(<1µM) | NSCLC | This inhibitor suppresses the expression of multiple RTKs in gefitinib-resistant NSCLC cells by enhancing the colocalization between Ub and target RTKs. | [196] | |
| HCC | This inhibitor enhances the efficacy of DOX or sorafenib by reducing the expression levels of RTKs. | [90] |
