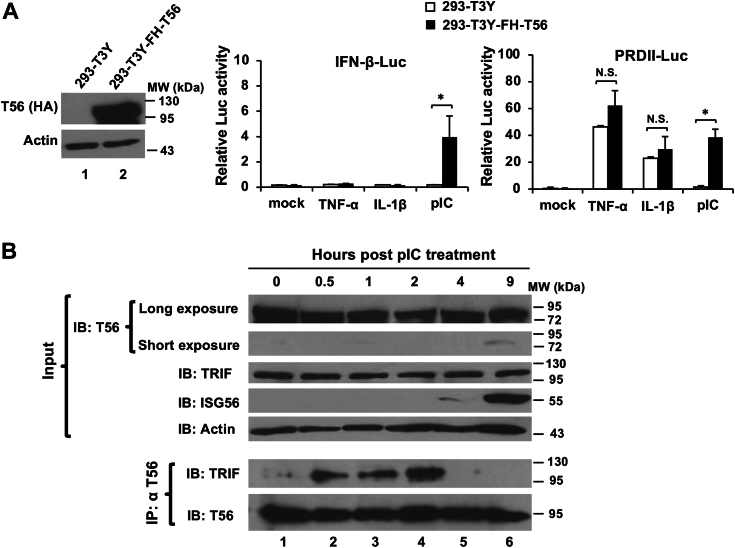
Figure 2.
TRIM56 potentiates activation of both IRF3 and NF-κB branches downstream of TLR3 signaling by forming a complex with TRIF early after engagement of the pathway.A, (Left panel) immunoblot analysis of the expression of N-terminally Flag-HA-tagged TRIM56 (FH-T56) using mouse anti-HA mAb in HEK293-TLR3-YFP (293-T3Y)-derived stable cells (293-T3Y-FH-T56) overexpressing FH-T56. HEK293-T3Y-FH-T56 and its parental 293-T3Y cells were cotransfected with internal control plasmid pRL-TK and reporter plasmid IFN-β-Luc (middle panel) or NF-κB responsive reporter plasmid PRDII-Luc (right panel), followed by mock treatment or treatment with TNF-α, IL-1β, or poly-I:C for 8 h. Dual luciferase reporter assay was then performed to measure the corresponding promoter activation. B, co-immunoprecipitation analysis of the interaction of endogenous TRIM56 with endogenous TRIF in HeLa cells at indicated time points post poly-I:C stimulation. Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated (IP) with anti-TRIM56 pAb, followed by immunoblotting (IB) with anti-TRIF or anti-TRIM56. The upper panels show expression of TRIM56, TRIF, IFN-stimulated gene 56 (ISG56), and actin in cell lysates. Single asterisk indicates that statistical differences exist between mock- and poly-I:C-treated cells with a p value of < 0.05. N.S., not statistically significant; pIC, poly-I:C. IFN, interferon; IRF, interferon regulatory factor; TLR, Toll-like receptor; TRIM56, tripartite-motif protein-56.