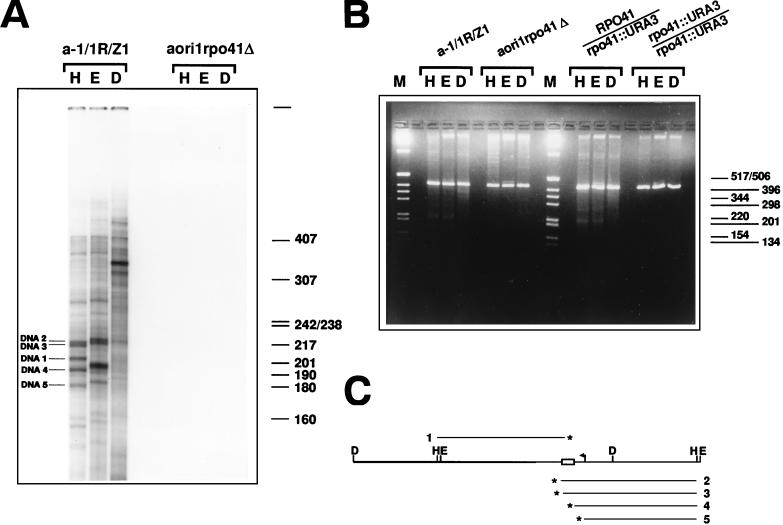
FIG. 5.
Detection of transcription-dependent 3′ DNA ends and DSBs in the mtDNA of strain a-1/1R/Z1. (A) Detection of 3′ ends in the mtDNA from a-1/1R/Z1 and aori1rpo41Δ. The 3′-end-labeled samples were restricted with HpaII (H), EcoRV (E), and DraI (D) prior to denaturation and electrophoresis on a denaturing polyacrylamide gel. The five DNA strands whose polarities were determined and whose 3′ ends were mapped are indicated (DNA1 to DNA5). The indicated size markers are those of 32P-labeled HpaII fragments of pBR322 DNA. (B). Detection of DSBs in the mtDNA of various derivatives of a-1/1R/Z1. Portions (480 ng) of mtDNA from strains a-1/1R/Z1 and aori1rpo41Δ, as well as the diploids 2n RPO41/rpo41::URA3 and 2n rpo41::URA3/rpo41::URA3 were digested with HpaII (H), EcoRV (E), or DraI (D) and displayed on a 2% agarose gel under nondenaturing conditions. In addition to the 416-bp repeat unit generated upon digestion with these single cutters, smaller DNA fragments can also be seen, whose presence depends upon a functional RPO41. M, molecular weight markers (1-kb DNA ladder; Gibco BRL). (C) Schematic diagram showing the map position and polarity for five DNA strands identified by 3′ end labeling. The polarity of each strand was determined from the size of the species obtained after digestion with HpaII and EcoRV, and the restriction map of the repeat unit. A fragment covering a little more than one repeat unit of the tandemly repeated ori1 genome was drawn so that the map positions of strands of both polarities could be shown relative to the HpaII and EcoRV sites. The asterisks indicate the 3′ end of each DNA (numbered 1 to 5). Details of the repeat unit are the same as in Fig. 1A.