Figure 1. Decision-making in CS.
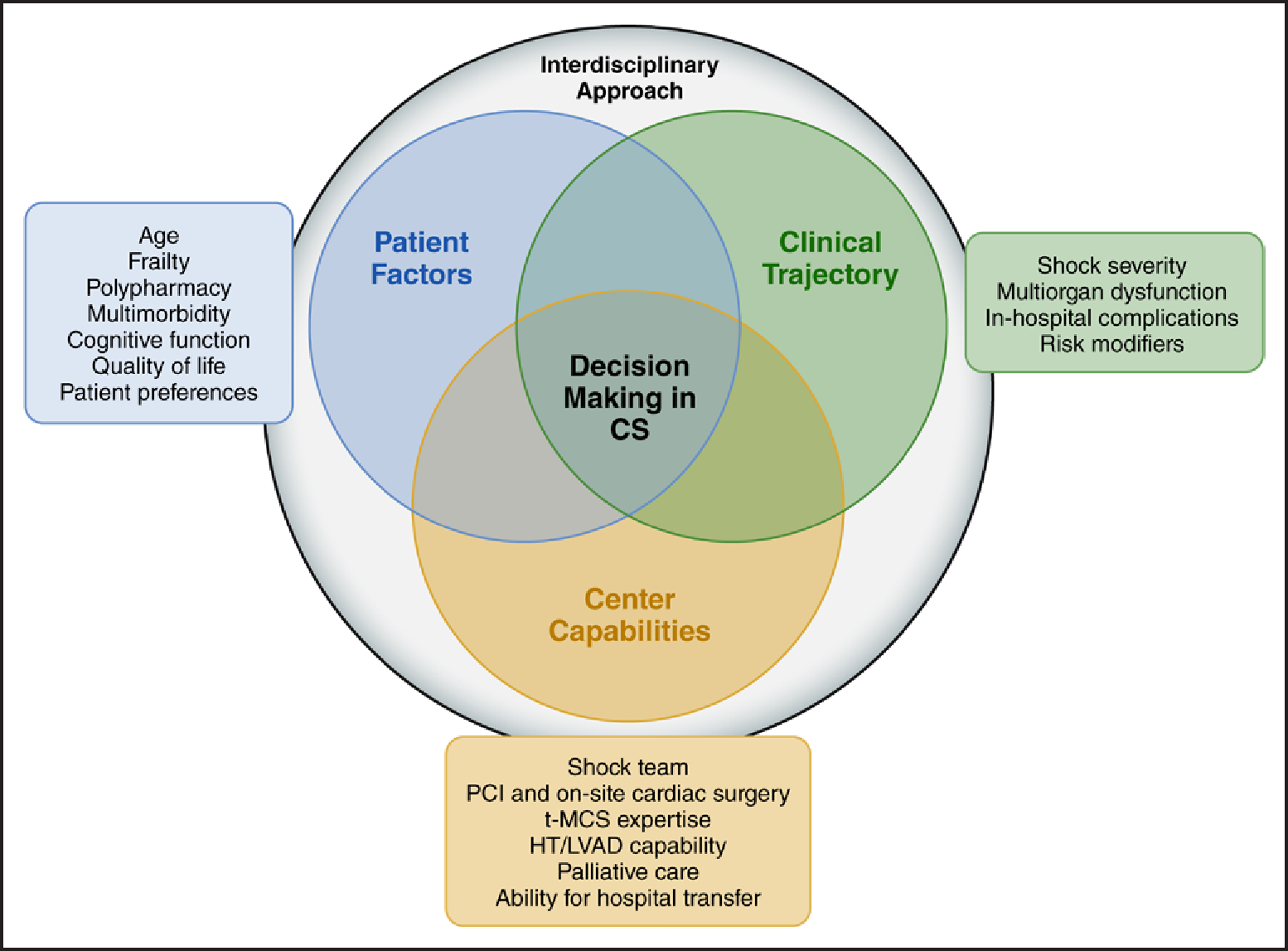
Risk assessment in cardiogenic shock (CS), especially among older adults, necessitates an interdisciplinary approach. The decision-making process involves considering individual patient factors, relevant aspects of the clinical trajectory, and the capabilities of the health care center. This comprehensive approach empowers health care professionals to customize care on the basis of each patient’s unique needs, to monitor the progression of the condition closely, and to use available resources effectively. By addressing the multifactorial challenges associated with the heightened mortality risk in older adults through an individualized and comprehensive interdisciplinary approach, health care professionals can optimize outcomes and enhance the overall management of CS in this subgroup. HT indicates heart transplantation; LVAD, left ventricular assist device; PCI, percutaneous coronary intervention; and t-MCS, temporary mechanical circulatory support.
