Figure 2. Approach to management in CS.
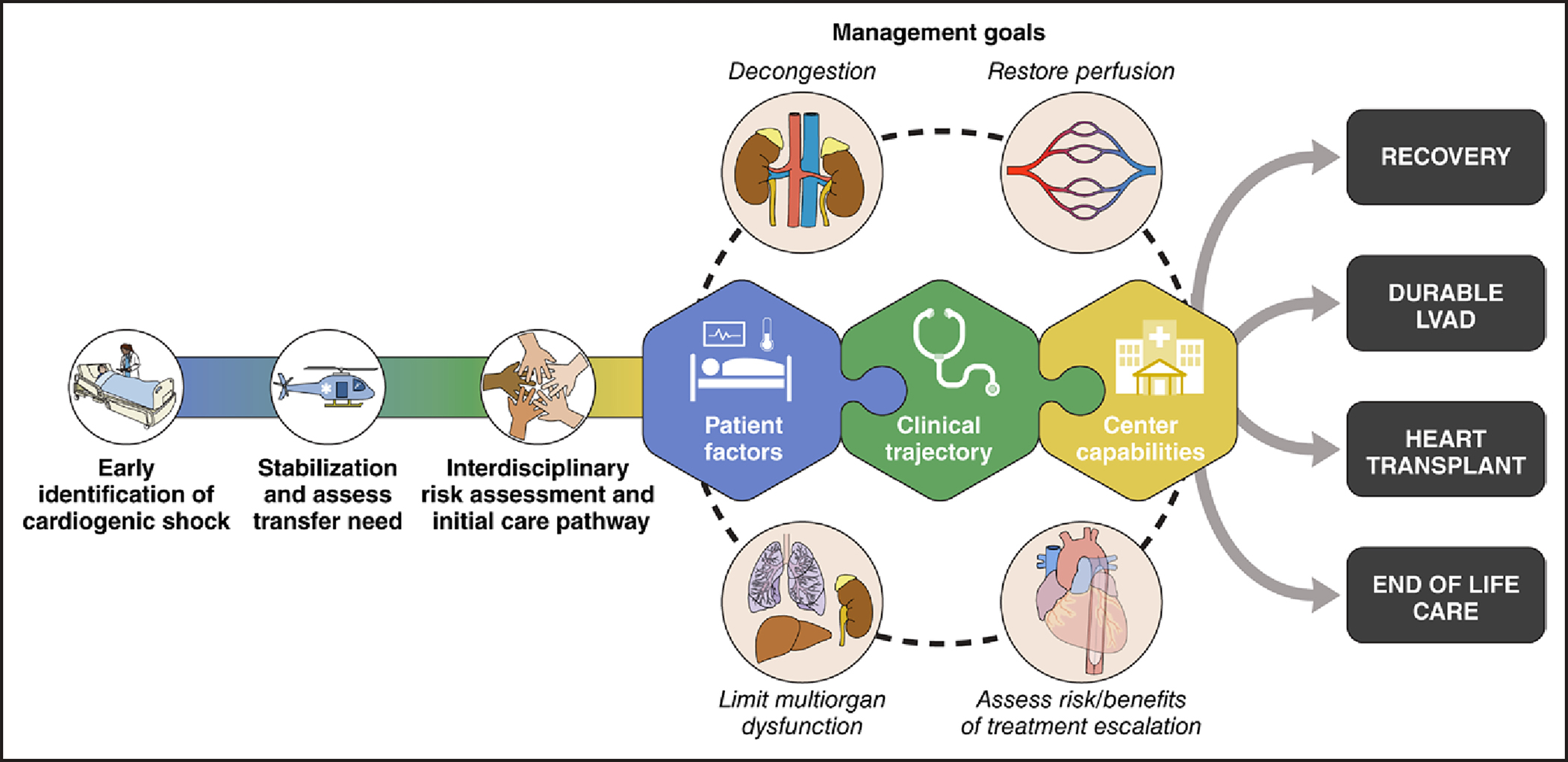
Regardless of age, the initial treatment approach for patients with CS should prioritize early recognition, initial stabilization, and timely identification of those requiring transfer to higher-level care. An interdisciplinary risk assessment and implementation of appropriate care pathways should be tailored to individual phenotypes. The management goals encompass decongestion, restoration of perfusion, limitation of multiorgan dysfunction, and evaluation of the risks and benefits of treatment escalation. Taking into account patient factors, clinical trajectory, and center capabilities, potential exit strategies may include recovery, the use of durable LVAD, heart transplantation, or transition to comfort care. CS indicates cardiogenic shock; and LVAD, left ventricular assist devices.
