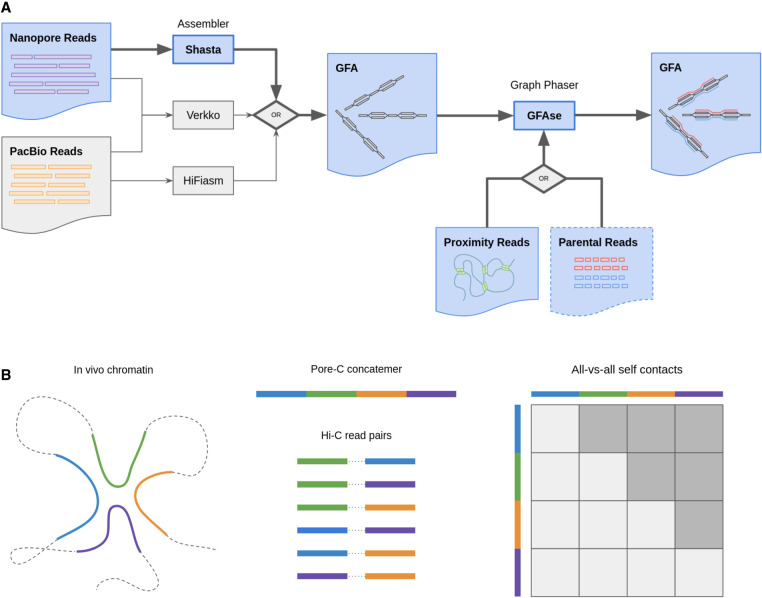
Figure 1.
Summary of de novo phasing pipeline using Shasta and GFAse and input proximity ligation data types Pore-C and Hi-C. (A) Shasta performs de novo assembly and phases to the extent that is supported by informative variants in the nanopore reads. GFAse then takes a partially phased assembly GFA and extends phasing using orthogonal phasing information. GFAse can perform phasing based on any alignable data type (Hi-C, Pore-C, etc.). For Shasta graphs, GFAse can also use parental sequencing. The pathways with bolded arrows and blue fill are the methods that are previously undescribed. (B) Diagram of Pore-C sequencing in comparison to Hi-C. In the all-versus-all contact matrix, shaded squares represent usable contacts, which scale at a rate of 1/2n2 − n for a concatemer of n fragments or subreads.