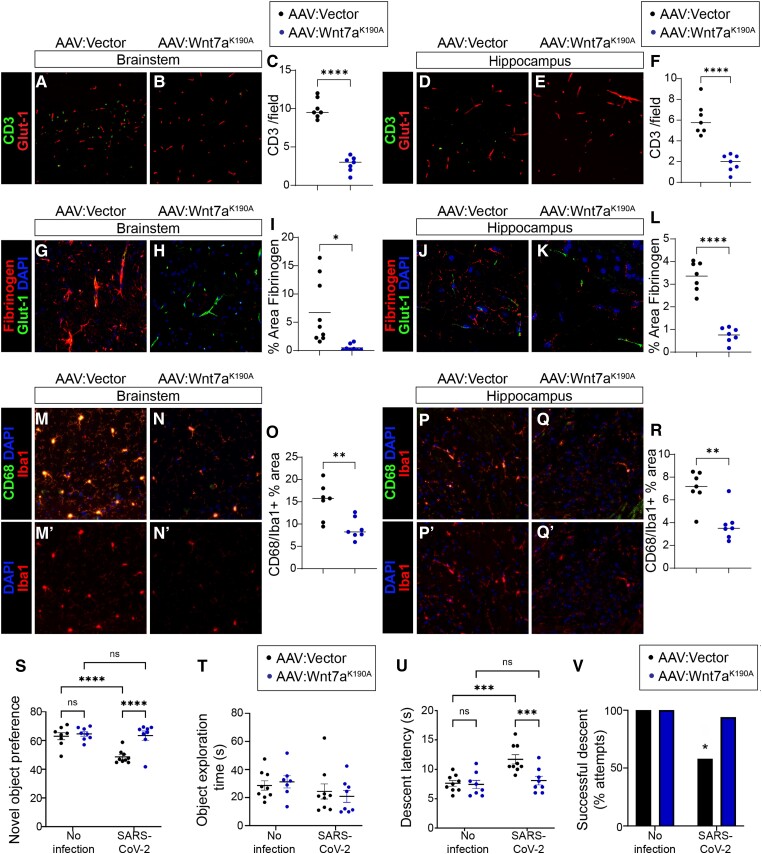
Figure 3.
Cerebrovascular-targeted engineered Wnt7aK190A protects against neurobehavioural impairment, neuroinflammation and blood–brain barrier leakage in SARS-CoV-2 infection. Mice were treated with AAV-PHP.eB vector control or AAV-PHP.eB-Wnt7aK190A 18 days prior to inoculation with SARS-CoV-2. Behavioural assessment and tissue collection was conducted 5 days after SARS-CoV-2 inoculation. (A–F) Immunostaining for CD3+ T cells (green) in brainstem (A–C) and hippocampus (D–F) of SARS-CoV-2 infected mice treated with AAV-PHP.eB-Wnt7aK190A or AAV-PHP.eB vector control. Glut-1 (red) was used to visualize endothelial cells. SARS-CoV-2 infected AAV-PHP.eB-Wnt7aK190A treated mice had significantly lower density of CD3+ T cells than did AAV-PHP.eB vector control treated mice in brainstem (C) and in hippocampus (F). Each dot represents the average value obtained from two to three tissue sections per mouse. Line indicates group mean. Unpaired Student’s t-test, ****P < 0.0001. (G–L) Immunostaining for fibrinogen (red) in brainstem (G–I) and hippocampus (J–L) of SARS-CoV-2 infected mice treated with AAV-PHP.eB-Wnt7aK190A or AAV-PHP.eB vector control. Glut1 (green) was used to visualize endothelial cells. SARS-CoV-2 infected AAV-PHP.eB-Wnt7aK190A treated mice had significantly lower perivascular fibrinogen than did AAV-PHP.eB vector control treated mice in brainstem (I; unpaired t-test with Welch’s correction for unequal variance, *P < 0.05) and in hippocampus (L, unpaired t-test, ****P < 0.0001). Each dot represents the average value obtained from two to three tissue sections per mouse. Line indicates group mean. (M–R) Immunostaining for CD68 (green), Iba1 (red), and DAPI (blue) in brainstem (M and N) and hippocampus (P and Q) of SARS-CoV-2 infected mice treated with AAV-PHP.eB-Wnt7aK190A or AAV-PHP.eB vector control. (O and R) Quantification of percent Iba1+ area that is positive for CD68. SARS-CoV-2 infected AAV-PHP.eB-Wnt7aK190A treated mice had significantly lower CD68/Iba1 than did AAV-PHP.eB vector control treated mice in brainstem (O; unpaired t-test, **P < 0.01) and in hippocampus (R; unpaired t-test, **P < 0.01). Each dot represents the average value obtained from two to three tissue sections per mouse. Line indicates group mean. Monochromatic images are provided in Supplementary Fig. 6. (S) The novel object recognition test for learning and memory was conducted in mice treated with AAV-PHP.eB-Wnt7aK190A or AAV-PHP.eB vector control without or with SARS-CoV-2 infection. There was a Treatment [F(1,29) = 13.05, P = 0.0011], SARS-CoV-2 [F(1,29) = 11.75, P = 0.0018], and Treatment × SARS-CoV-2 interaction [F(1,29) = 8.397, P = 0.0071] for novel object preference. Post hoc analysis revealed that SARS-CoV-2 infection impaired novel object recognition in mice treated with the vector control (****P < 0.0001) but not in mice treated with AAV-PHP.eB-Wnt7aK190A (P = 0.7145). Indeed, SARS-CoV-2 infected mice treated with AAV-PHP.eB-Wnt7aK190A performed significantly better than SARS-CoV-2 infected mice treated with the control vector (****P < 0.0001). (T) Total object exploration was not significantly influenced by Treatment [F(1,29) = 0.009622, P = 0.9225], SARS-CoV-2 [F(1,29) = 2.679, P = 0.1125], or Treatment × SARS-CoV-2 interaction [F(1,29) = 0.4577, P = 0.5041], supporting that the novel object recognition task was not confounded by lack of interest or impaired motility. (U) Pole descent latency, a measure of complex motor coordination impairment, was significantly influenced by Treatment [F(1,30) = 7.855, P = 0.0088], SARS-CoV-2 [F(1,30) = 12.10, P = 0.0016], and Treatment × SARS-CoV-2 interaction [F(1,30) = 6.410, P = 0.0168]. Post hoc analysis revealed the difference was driven by impairment in the vector-treated SARS-CoV-2 group as compared to the AAV-PHP.eB-Wnt7aK190A treated group (***P < 0.001) or the uninfected group (***P < 0.001). (V) SARS-CoV-2 infected mice treated with AAV-PHP.eB-Wnt7aK190A fell off the pole significantly fewer times than those treated with AAV-PHP.eB vector control (Fisher’s exact test, *P = 0.0198).