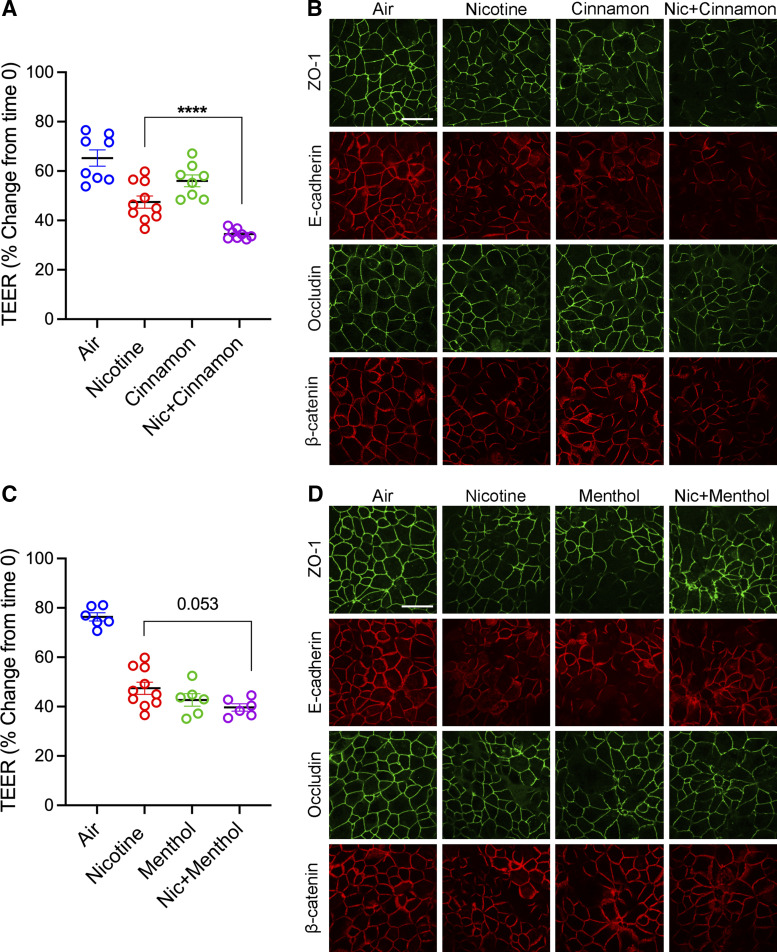
Figure 6.
Exposure to flavor in e-cig liquid induced barrier dysfunction and exaggerated e-cig nicotine-induced airway barrier dysfunction. A: confluent 16HBE cells were exposed to aerosolized e-cig nicotine, cinnamon, or e-cig nicotine mixed with cinnamon or HEPA-filtered air three times for 24 h. TEER (Ω × cm2) was measured 24 h postexposure and plotted as a percentage change from time 0. B: at 24 h postexposure, 16HBE cells were fixed with methanol and immunolabeled for tight junction proteins (ZO-1 and occludin) and adherens junction proteins (E-cadherin and β-catenin) and imaged by confocal microscopy. C: confluent 16HBE cells were exposed to aerosolized e-cig nicotine, menthol, or e-cig nicotine mixed with menthol or HEPA-filtered air three times for 24 h. TEER was measured at 24 h postexposure and plotted as a percentage change from time 0. D: at 24 h postexposure, 16HBE cells were fixed with methanol and immunolabeled for tight junction proteins (ZO-1 and occludin) and adherens junction proteins (E-cadherin and β-catenin) and imaged by confocal microscopy. Data are presented as means ± SE, n = 6–10, one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test. ****P < 0.0001. The images are representative of at least three independent experiments. Scale bar, 30 μm. TEER, transepithelial electrical resistance; 16HBE, 16HBE14o- human bronchial epithelial.