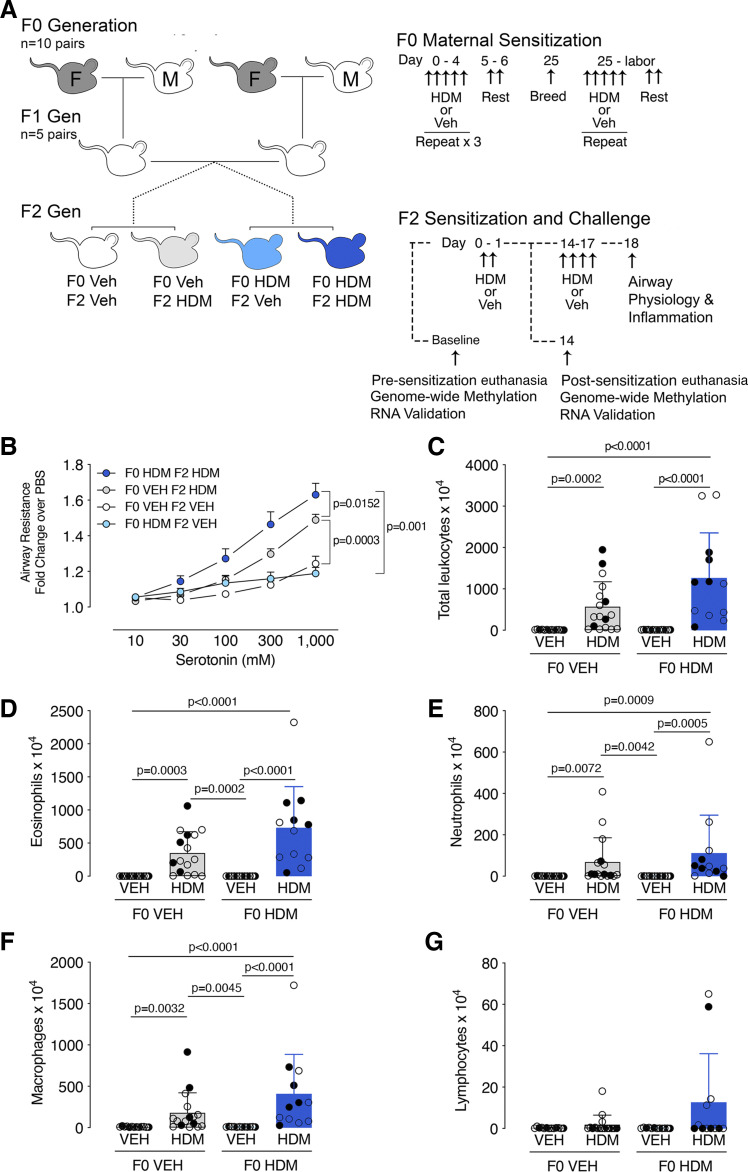
Figure 1.
Allergen-induced airway hyperreactivity and inflammation is potentiated in second-generation offspring of house dust mite (HDM)-exposed founders. A: female F0 mice (gray mice, “F”) were exposed to intranasal house dust mite (HDM) or vehicle (Veh) for five consecutive days followed by two days of rest for 4 wk, mated, and then exposed to HDM or vehicle 5 days per week through gestation until birth. Male F0 mice (white mouse, “M”) received no treatment. Nonlittermate F1 male and female offspring from matching F0 maternal treatment groups were randomized into breeding pairs and received no treatments. Male and female F2 offspring were sensitized to HDM or treated with Veh on days 0 and 1 and then challenged with HDM (F0Veh•F1HDM and F0 HDM•F1HDM) or vehicle (F0Veh•F1Veh and F0HDM•F1 Veh) on days 14–17. Airway physiology and bronchoalveolar lavage leukocytes were measured on HDM-sensitized and challenged F2 mice (protocol day 18). A subset of F2 mice were euthanized before allergen sensitization (F0Veh•F1Base and F0HDM•F1Base) and after HDM sensitization (sensitized both day 0 and 1, euthanized day 14; F0Veh•F1Sens and F0HDM•F1Sens) for methylation experiments. B: F2 airway resistance measured in response to aerosolized serotonin. Airway hyperreactivity was present in both HDM-challenged F2 groups (F0Veh•F2HDM and F0HDM•F2HDM). However, HDM-induced airway hyperreactivity was significantly potentiated in HDM-sensitized F2 mice from HDM-exposed F0 mice (F0HDM•F2HDM) compared with F2 mice from vehicle-exposed F0 mice (F0Veh•F2HDM). F0Veh•F2Veh, n = 13, n = 6 males and n = 7 females. F0Veh•F2HDM n = 20, n = 6 females, n = 14 males. F0HDM•F2Veh n = 13, n = 6 males and n = 7 females. F0HDM•F2HDM n = 18, n = 10 males and n = 8 females. Data analyzed with two-way ANOVA with repeated measures. Total (C) and differential (D–G) inflammatory cells and counts were measured in bronchoalveolar lavage of F2 mice. Data were analyzed using Kruskal–Wallis ANOVA with a Dunn’s post test. Closed and open circles represent females and males, respectively.