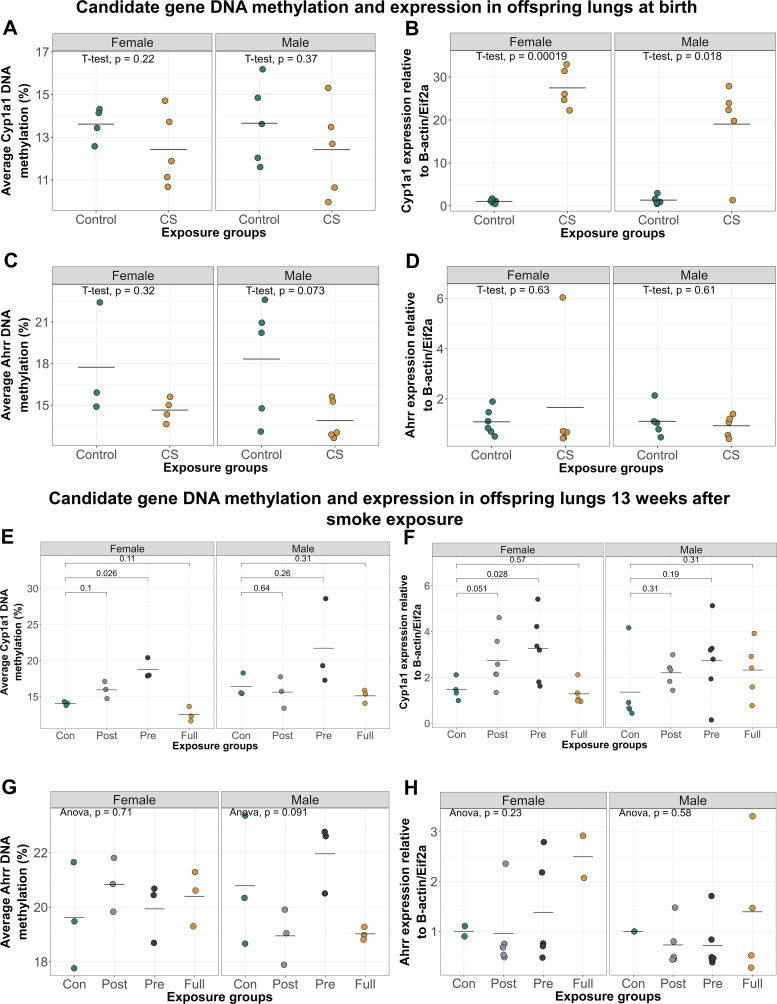
Figure 4.
Early-life exposure to CS significantly alters lung Cyp1a1 expression at birth and Cyp1a1 DNAm 13 wk after smoke cessation. A: Cyp1a1 DNAm in offspring lungs at birth (N = 10 control, N = 10 CS). B: Cyp1a1 expression in offspring lungs at birth was significantly increased in CS-exposed males (N = 5, mean = 19.00, SD = 10.30) and females (N = 5, mean = 27.50, SD = 4.54) offspring, compared with control males (N = 5, mean = 1.36, SD = 0.93) and control females (N = 5, mean = 1.47, SD = 0.43). C: Ahrr DNAm in offspring lungs at birth (N = 8 control, N = 10 CS). D: Ahrr expression in offspring lungs at birth (N = 10 control, N = 10 CS). E: Cyp1a1 DNAm in offspring lungs at 16 wk of age. Prenatal and postnatal CS exposure caused an increase in female lung Cyp1a1 DNAm, whereas fully exposed offspring showed a decrease. Only prenatally exposed female offspring had significantly elevated Cyp1a1 DNAm (mean = 18.80, SD = 1.42) compared with control females (mean = 14.10, SD = 0.26). N = 3 per group. F: Cyp1a1 expression in offspring lungs at 16 wk of age. Prenatally exposed female offspring had significantly elevated lung Cyp1a1 expression levels (mean = 3.28, SD = 1.44) compared with control females (mean = 1.48, SD = 0.47). N = 3–6 per group. G: Ahrr DNAm in offspring lungs at 16 wk of age. N = 3 per group. H: Ahrr expression in offspring lungs at 16 wk of age. N = 3–6 per group. One-way ANOVA was used to compare DNAm values between groups (P < 0.05 was significant), followed by two-group comparisons where significant. CS, cigarette smoke.