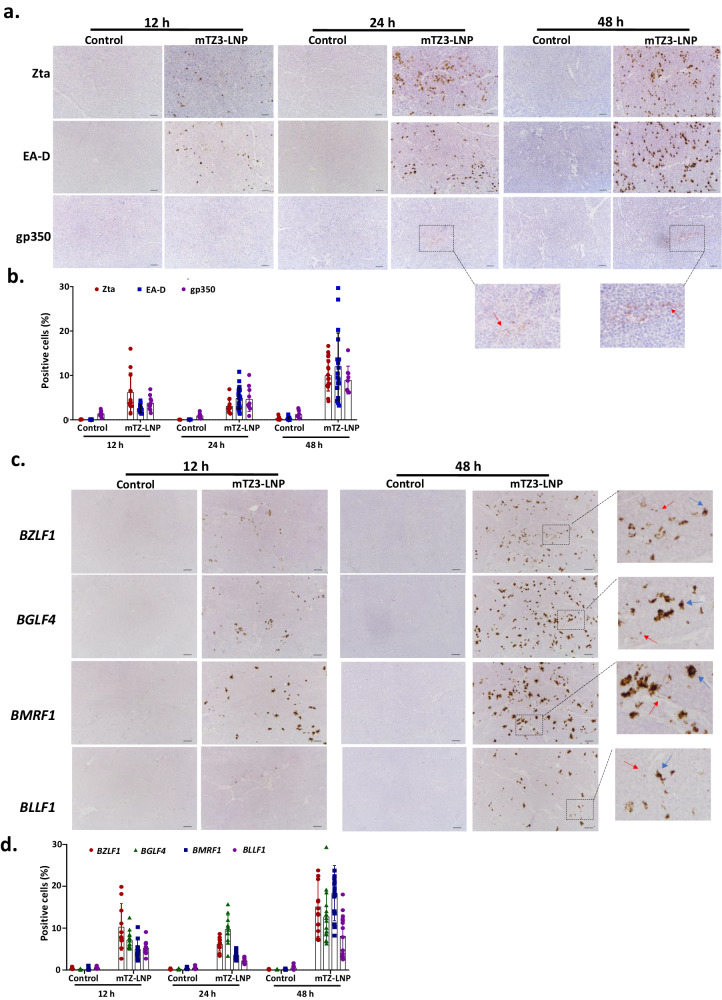
Fig. 6. mTZ3-LNP reactivates EBV lytic gene expression in in vivo EBV-positive tumor models.
a Using immunohistochemical staining, the expression of Zta, EA-D, and gp350 was detected in the representative tissue sections of SNU719 tumors from NOD-SCID mouse models at 12, 24, and 48 h after the intravenous administration of mTZ3-LNP (n = 3 mice/group). The tumor cells with gp350 expression were illustrated by red arrows. Scale bar = 50 μm. b The percentages of tumor cells with Zta, EA-D, and gp350 expression in the tumors from the mice were determined at 12, 24, and 48 h post-intravenous administration of mTZ3-LNPs. At least four different representative fields (×200 magnification) obtained from the section of each triplicate were counted (n = at least 4 fields/tumor examined over 3 mice). Data are presented as mean ± SD. c The expression of EBV immediate early (BZLF1), early (BMRF1 and BGLF4), and late (BLLF1) lytic gene transcripts in representative FFPE sections of SNU719 tumors from NOD-SCID mouse models at 12 and 48 h post-treatment with mTZ3-LNP was determined using RNAscope RNA in-situ hybridization (n = 3 mice/group). Representative tumor cells expressing high and low copy numbers of EBV lytic gene transcripts are indicated by blue and red arrows respectively. Scale bar = 50 μm. d The percentages of tumor cells expressing BZLF1, BGLF4, BMRF1, and BLLF1 mRNAs in the tumors from the mice were determined at 12, 24, and 48 h post-treatment with mTZ3-LNP. At least four different representative fields (×200 magnification) obtained from the section of each triplicate were counted (n = at least 4 fields/tumors examined over 3 mice). Data are presented as mean ± SD. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.