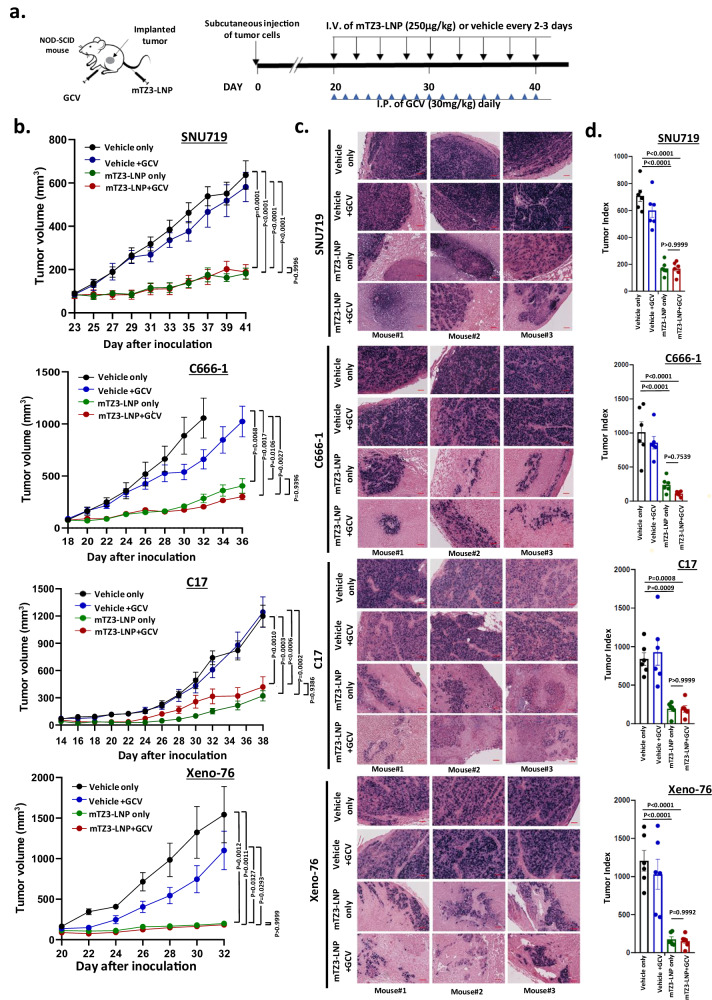
Fig. 7. In vivo inhibition of EBV-positive epithelial cancers by mTZ3-LNP-based lytic induction treatment.
a A scheme illustrating the in vivo treatment of EBV-positive EBVaGC (SNU719) and NPC (C666-1, C17, Xeno-76) preclinical xenograft NOD-SCID mouse models with mTZ3-LNP and GCV. b Tumor volumes were measured throughout the treatment period (SNU719 and C666-1: n = 7 mice/group; C17 and Xeno-76: n = 6 mice/group). Data are presented as mean ± SEM. A P < 0.05 was considered to indicate statistical significance. c Using EBER in-situ hybridization, EBV-positive tumor cells were detected in representative FFPE sections of residual tumors harvested after treatment. Scale bar = 250 μm. Representative images from n = 6–7 mice/group are shown. d The tumor index of each harvested EBV-positive tumor was determined after treatment with mTZ3-LNP alone, combined mTZ3-LNP and GCV, GCV, and vehicle controls. Tumor index = tumor volume × percentage of the EBER-positive area. Significant tumor growth inhibition was observed in SNU719, C666-1, C17, and Xeno-76 xenografts treated with mTZ3-LNP alone or combined with GCV (SNU719 and C666-1: n = 7 mice/group; C17 and Xeno-76: n = 6 mice/group). Data are presented as mean ± SD. ns not significant; A P < 0.05 was considered to indicate statistical significance. One-way analysis of variance (ANOVA). Source data are provided as a Source Data file.