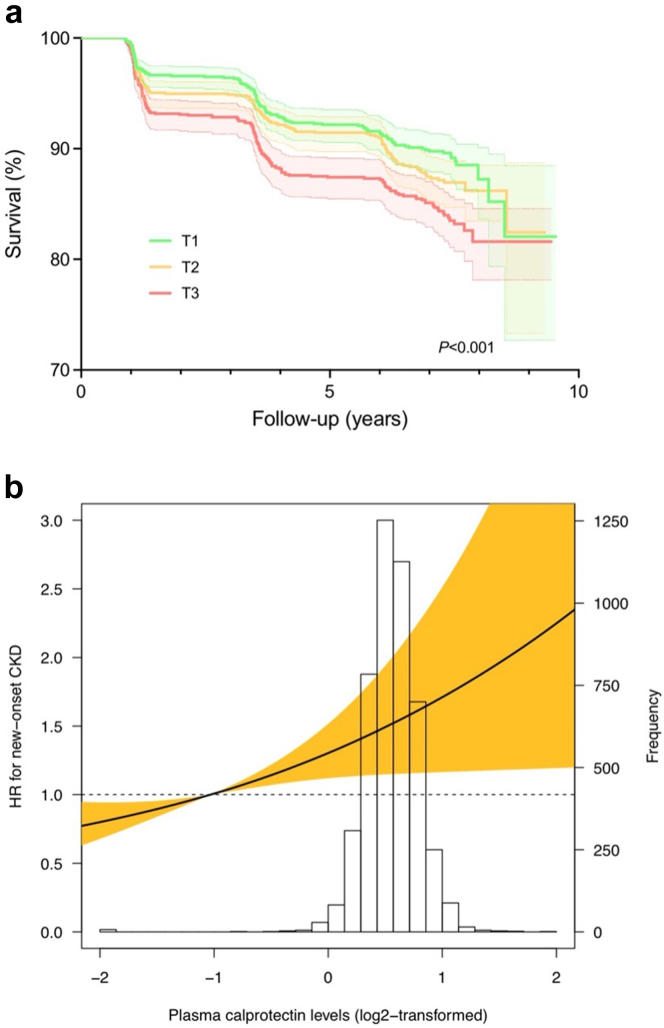
Figure 1.
Plasma calprotectin levels associate with an increased risk of new-onset CKD. (a) Kaplan-Meier survival curves for the association between plasma calprotectin levels and the risk of new-onset CKD based on the composite outcome (eGFR, UAE or both) The highest rate of new-onset CKD was observed in the highest tertile (T3) of plasma calprotectin levels. (b) Restricted cubic splines (RCS) were fitted to test for potential nonlinearity of the association between plasma calprotectin levels and the risk of new-onset CKD. Estimated associations were derived from the Cox proportional hazards regression models and RCS with 3 knots (set at the 1st, 50th, and 99th percentiles). A likelihood ratio test for nonlinearity was nonsignificant for this model (χ2 = 0.08, P = 0.773). Shaded areas of the RCS curve represent the 95% confidence intervals. CKD, chronic kidney disease; eGFR, estimated glomerular filtration rate; HR, hazard ratio; UAE, urinary albumin excretion