FIGURE 2.
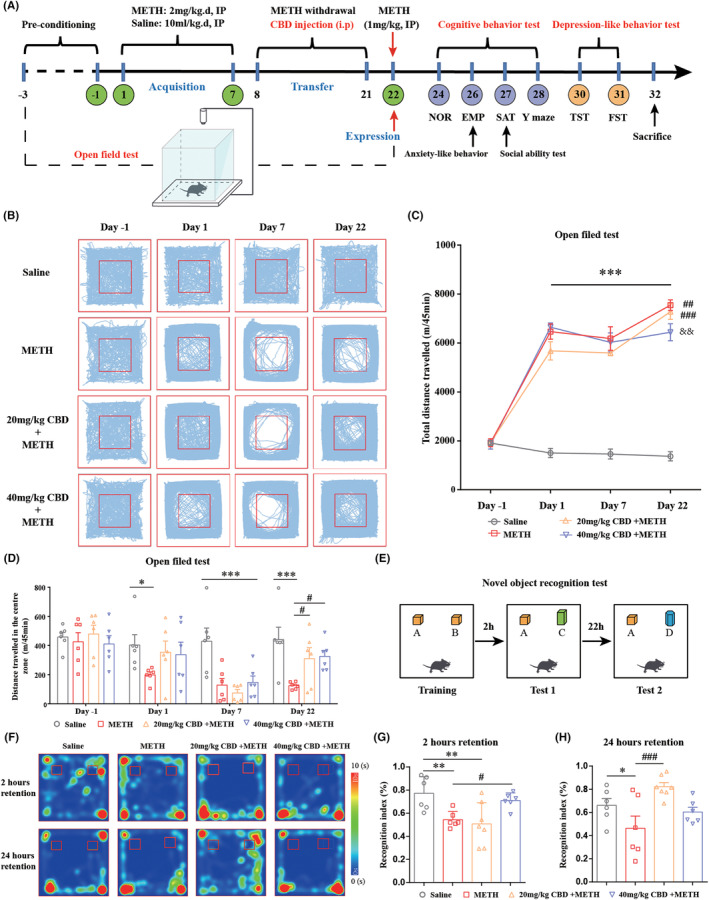
Chronic administration of CBD reduces METH‐induced locomotor sensitization, anxiety‐like behavior, and cognitive impairments in mice. (A) The schedule of locomotor sensitization, mood, and cognitive function tests. (B) The tracks of mice in the open‐field apparatus. (C) Chronic administration of CBD (40 mg/kg, but not 20 mg/kg) reduced METH‐induced locomotor sensitization in mice. ***p < 0.001 versus saline group on the same day; ## p < 0.01, ### p < 0.001 versus same group on day 7; && p < 0.01 versus METH group on day 22. (D) Chronic administration of CBD alleviated METH‐induced anxiety‐like behavior in mice. *p < 0.05, ***p < 0.001; # p < 0.05. (E) The protocol of NOR test. (F) Heat maps of mice's track in the NOR test. (G) Chronic administration of CBD (40 mg/kg, but not 20 mg/kg) improved the reduction of recognition index (%) induced by METH after 2 h of training. **p < 0.01; # p < 0.05. (H) Chronic administration of CBD (20 mg/kg, but not 40 mg/kg) improved the reduction of recognition index (%) induced by METH after 24 h of training. *p < 0.05; ### p < 0.001. The data were analyzed by two‐way ANOVA (C–D) or one‐way ANOVA (G–H) followed by Tukey's multiple comparison test; all values are presented as the mean ± SEM (n = 6–8).
