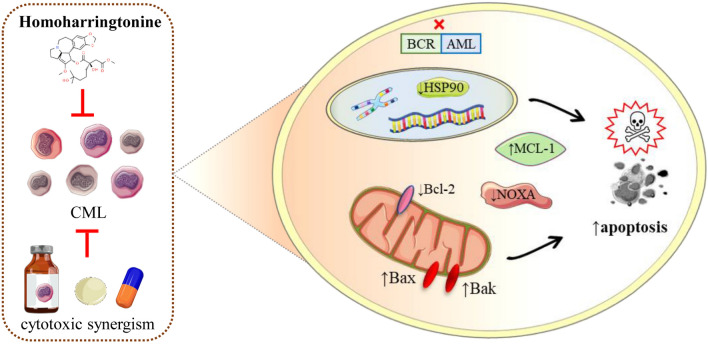
Fig. 6.
Impact of HHT on apoptosis induction in CML. HHT disrupts the BCR–ABL oncogenic signaling in CML, leading to the inhibition of the Heat Shock Protein 90 (HSP90) chaperone function. This disruption contributes to the downregulation of Myeloid Cell Leukemia 1 (MCL-1) and upregulation of NOXA, both of which are key regulators of apoptosis. Furthermore, the figure depicts the increase in Bcl-2-associated X Protein (Bax) and the activation of BAK, triggering the apoptosis cascade. The combination of HHT with other cytotoxic agents is shown to result in a synergistic effect, enhancing the apoptotic response in CML cells. Abbreviations and symbols: HHT: Homoharringtonine; CML: Chronic Myeloid Leukemia; BCR–ABL: Breakpoint Cluster Region–Abelson; HSP90: Heat Shock Protein 90; MCL-1: Myeloid Cell Leukemia 1; NOXA: Latin for “damage,” a pro-apoptotic Bcl-2 family member; Bax: Bcl-2-associated X Protein; BAK: Bcl-2 homologous antagonist/killer; ↑: Increase/upregulation; ↓: Decrease/downregulation; X: Inhibition/blockage.