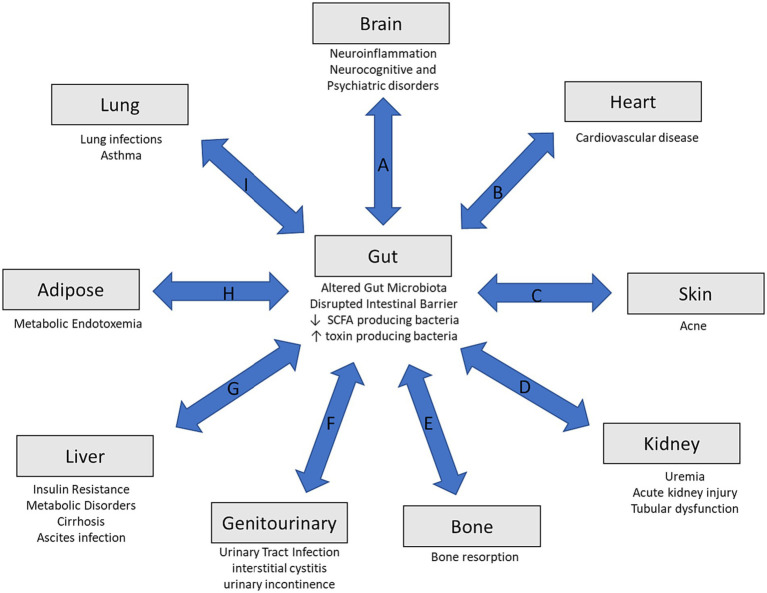
Figure 1.
Overview of the gut-organ axis. Disruptions in the gut microbiome can lead to a decrease number of short-chain fatty acid producing bacteria and increased toxin producing bacteria. Along with this, there may be disruptions in the intestinal barriers leading to bacterial translocation that may influence systemic inflammation. (A) The gut-brain axis, (B) gut-heart axis, (C) gut-skin axis, (D) gut-kidney axis, (E) gut-bone, (F) gut-genitourinary axis, (G) gut-liver axis, (H) gut-adipose, and (I) gut-lung axis.