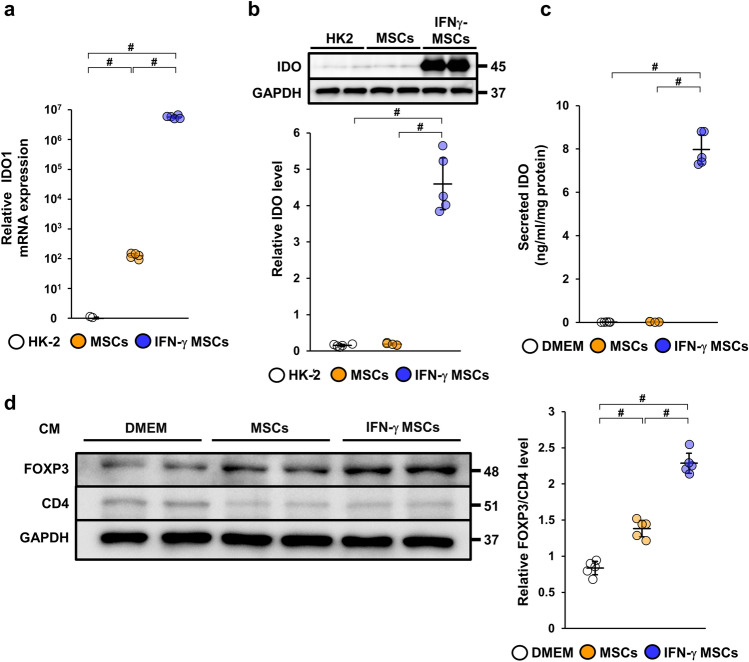
Figure 3.
Effects of conditioned medium obtained from IFN-γ MSCs on differentiation of naïve CD4 T cells into regulatory T cells. mRNA and protein levels of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO) were evaluated by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (a) and western blot (b) analyses. (a) Expression levels of IDO1 mRNA in HK-2 cells, MSCs, and IFN-γ MSCs (n = 5 in each group). (b) Western blot analysis of IDO in HK-2 cells, MSCs, and IFN-γ MSCs. Graph shows densitometric analysis of IDO expression levels normalized to the GAPDH expression level (n = 5 in each group). Full-length blots are presented in Supplementary Fig. 1d. (c) Concentration of IDO in conditioned medium from MSCs was evaluated by an ELISA analysis at 48 h after IFN-γ stimulation. DMEM containing 0.1% FBS was used as a negative control. Graph shows IDO concentrations in DMEM containing 0.1% FBS or conditioned medium from MSCs or IFN-γ MSCs (n = 5 in each group). (d) Differentiation of naïve CD4 T cells into regulatory T cells were evaluated by FOXP3 and CD4 protein levels. Naïve CD4 T cells were isolated from human peripheral blood mononuclear cells and were incubated with DMEM containing 0.1% FBS or conditioned medium obtained from MSCs or IFN-γ MSCs. Five days later, the cells were harvested and subjected to western blot analysis of FOXP3 and CD4. Graph shows densitometric analysis of FOXP3/CD4 expression levels normalized to the GAPDH expression level (n = 5 in each group). Full-length blots are presented in Supplementary Fig. 1e. Data indicate mean ± S.D. #P < 0.01 (one-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni’s post-hoc test).