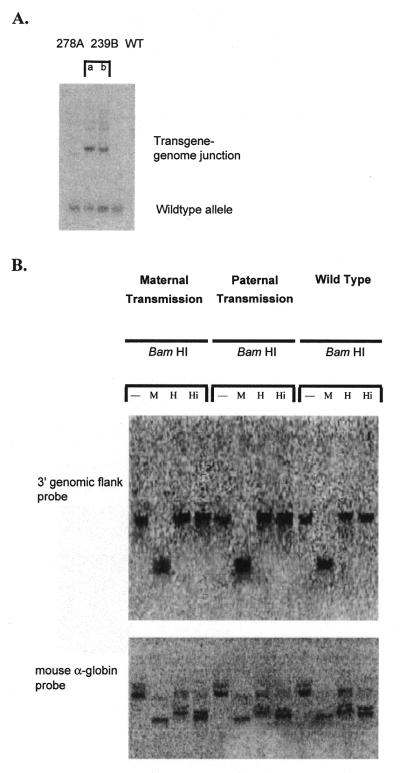
Figure 6.
(A) The 3′ genomic flank sequence is unique in the genome. Southern blotting of DraI-digested genomic DNA and hybridisation with a 301 bp radiolabelled HindIII–EcoRI fragment of the 3′ genomic sequence from the site of integration (obtained by LMPCR) generated a single band in DNA samples from line 278A and wild-type (WT) mice and two bands in DNA from line 239B. The 239B DNA was obtained from a hemizygous mouse so that one allele generated a wild-type band and the other band represents the transgene–genome junction. Samples a and b are independent samples from line 239B. (B) Susceptibility of the 3′ site of integration of the transgene to digestion by methylation-sensitive restriction enzymes. Transgenic embryos were collected following either maternal or paternal transmission of the transgene as well as their wild-type littermates. DNA extracted from these 12.5 d.p.c. embryos was digested with BamHI alone or in combination with either MspI (M) (methylation-insensitive), HpaII (H) (methylation-sensitive) or HinP1I (Hi) (methylation-sensitive). The membrane was hybridised using a radiolabelled 301 bp HindIII–EcoRI fragment of the 3′ genomic DNA from the site of integration (obtained by LMPCR). The membrane was stripped and reprobed with the radiolabelled mouse α-globin gene to check for complete digestion of the DNA in all samples.