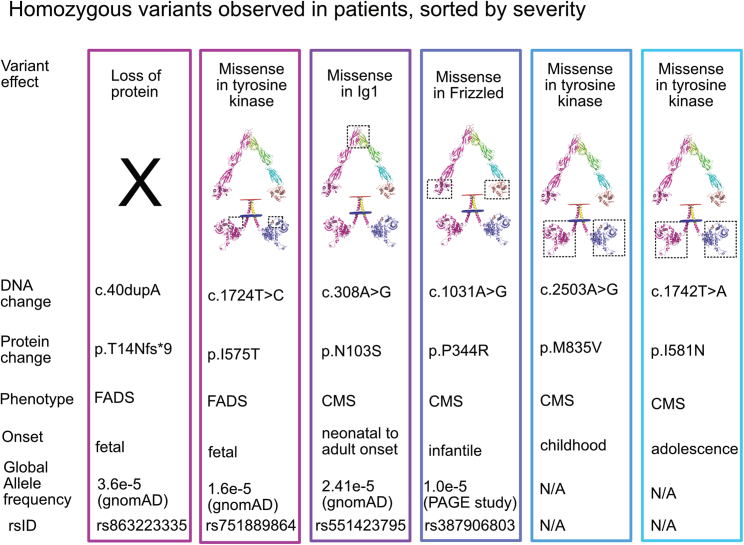
Figure 4.
Homozygous MUSK variants previously reported in patients
Six variants have been observed in a homozygous state. Two of these variants result in FADS (c.40dupA and c.1724T>C). The c.40dupA allele leads to a complete loss of protein expression. It is the only combination that leads to a complete loss of protein expression observed in patients to date, though presumably, any other combination that leads to complete loss of MuSK will be lethal in utero. The c.1724T>C allele leads to a p.I575T missense variant. This variant leads to the placement of a residue that is capable of being phosphorylated within two amino acids of the prototypically phosphorylated tyrosine at position 577. Further experimental validation of the p.I575T variant is needed to determine if it alters phosphorylation at Y577 or leads to disease through another mechanism. The remaining four variants result in CMS and are located within the Ig1, Frz-like, and kinase domains. The p.N103S variant is the most frequent of the homozygous variants and results in a range of symptom severity, from neonatal onset to adult onset.