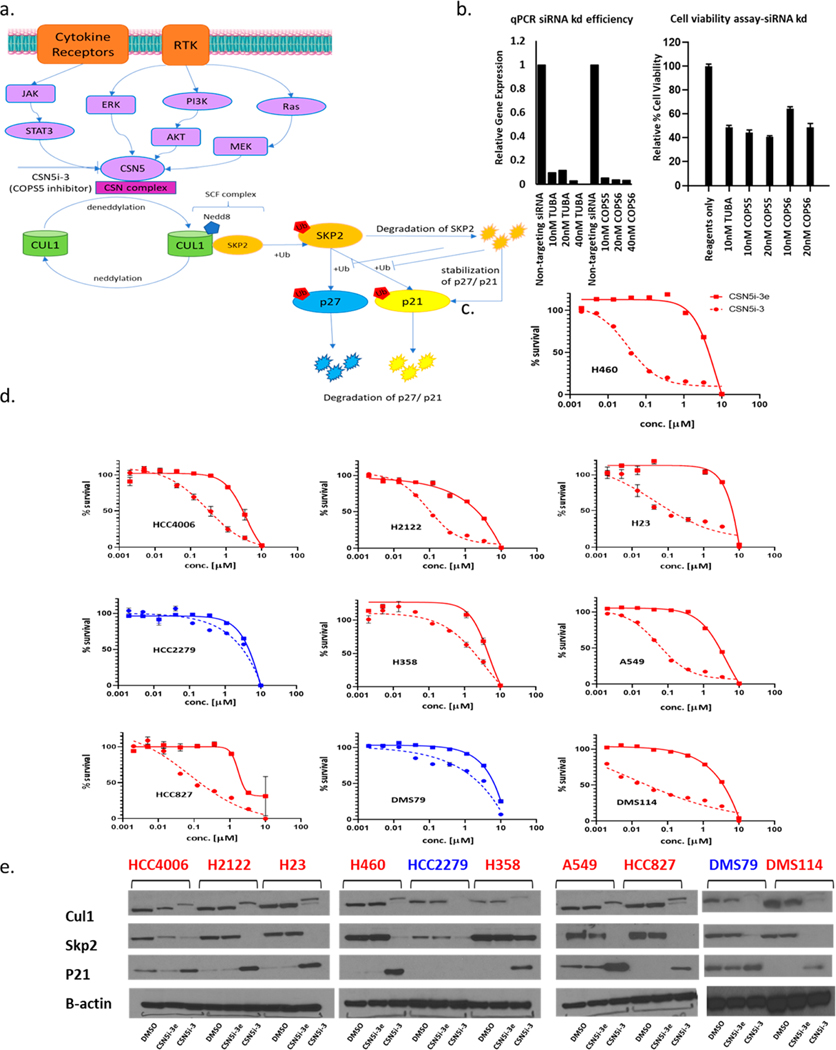
Figure 4.
Effect of COPS5 inhibition using CSN5i-3 and CSN5i-3e on NSCLC and SCLC cell lines. (a) Schematic representation of regulation of cullin neddylation and corresponding substrates by COPS5. (b) Effect of COPS5/COPS6 siRNA knockdown on cell viability in H460 cells. α-tubulin (TUBA) is used as a housekeeping gene control. (c) Effect of CSN5i-3 (active enantiomer) and CSN5i-3e (inactive enantiomer) on cell viability in H460 cells. (d) Effect of CSN5i-3 and CSN5i-3e on cell viability in a panel of NSCLC and SCLC cell lines. (e) Effect on substrates of Cul1 by CSN5i-3 and CSN5i-3e. In parts c−e the cell lines showing loss of viability due to CSN5i-3 treatment are shown in red and the cell lines unaffected by CSN5i-3 treatment are shown in blue.