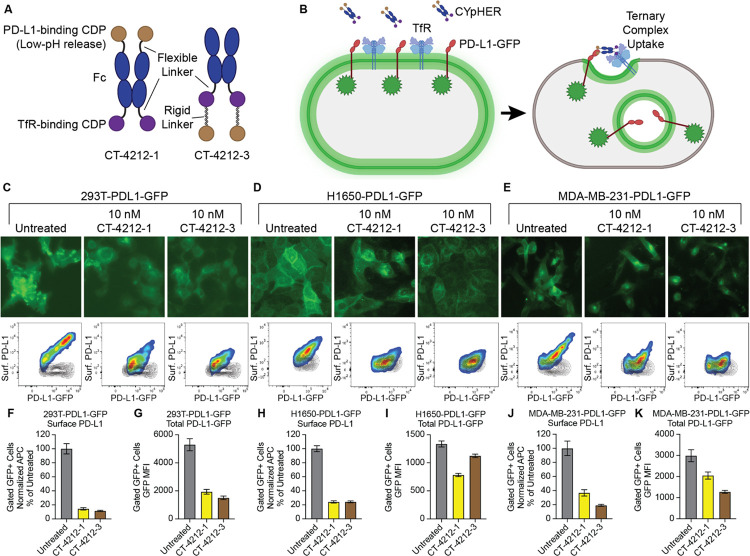
Fig. 2. PD-L1 CYpHER design and target depletion in cell pools overexpressing PD-L1-GFP.
(A) Two designs of PD-L1 CYpHERs, named CT-4212-1 and CT-4212-3, using a high-affinity TfR-binding CDP and a pH-dependent PD-L1-binding CDP. (B) Illustration of PD-L1-GFP trafficking induced by CYpHER. (C to E) Pools of 293T (C), H1650 (D), and MDA-MB-231 (E) cells transduced with lentivirus driving PD-L1-GFP were untreated or incubated with 10 nM CYpHER for 24 hr before GFP-channel microscopy (above) and flow cytometry (below) after staining for surface PD-L1. Black contour in flow profiles: cells stained without PD-L1 antibody. (F to K) Quantitation of normalized surface PD-L1 (F, H, and J) or total PD-L1-GFP (G, I, and K) signal in 293T-PDL1-GFP (F and G), H1650-PDL1-GFP (H and I), and MDA-MB-231-PDL1-GFP (J and K) cells with or without CYpHER treatment.