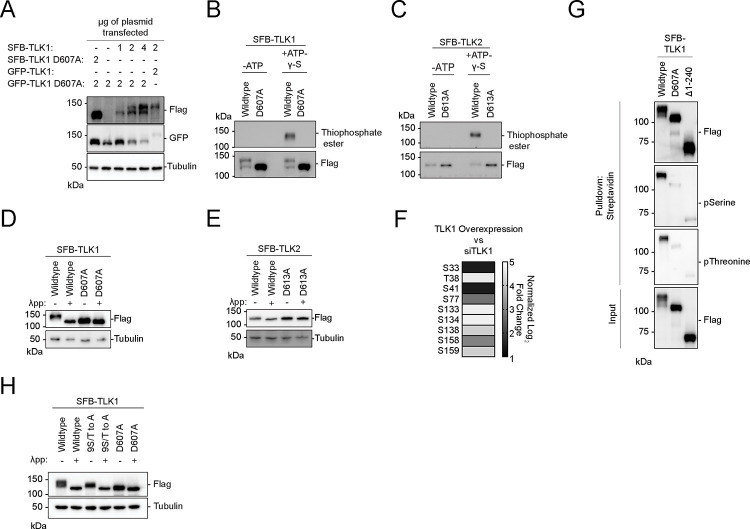
Figure 2. Tousled-like kinases are autophosphorylated at their N-terminus.
(A) Co-transfection of TLK1 wildtype and catalytic inactive mutant D607A with the indicated amount of plasmids in HEK293T cells followed by Western blotting analysis.
(B-C) Kinase assays using ATP-γ-S followed by alkylation by p-Nitrobenzyl mesylate to convert phosphorylated residues into thiophosphate esters. Antibody against thiophosphate ester was used to identify phosphorylation events.
(D-E) Lambda protein phosphatase (λpp) assay was performed using SFB-tagged TLK1 wildtype and D607A mutant or SFB-tagged TLK2 wildtype and D613A mutant purified from HEK293T cell lysate. Differential molecular weights were analyzed by Western blotting analysis.
(F) TLK1 is autophosphorylated at 9 residues within its N-terminus. Phospho-Tandem-Mass-Tag mass spectrometry was performed on phosphopeptides enriched from HEK293T cells with TLK1 overexpression and knockdown using siRNA.
(G) TLK1 N-terminus is highly phosphorylated. SFB-tagged TLK1 wildtype, D607A, or Δ1–240 (ΔN-terminus) were purified from HEK293T using streptavidin beads followed by Western blotting analysis using phospho-Serine and phospho-threonine antibodies.
(H) TLK1 wildtype, N-terminal 9S/T to A, and catalytic inactive mutants were treated with λ-phosphatase. Differential molecular weights were analyzed by Western blot.