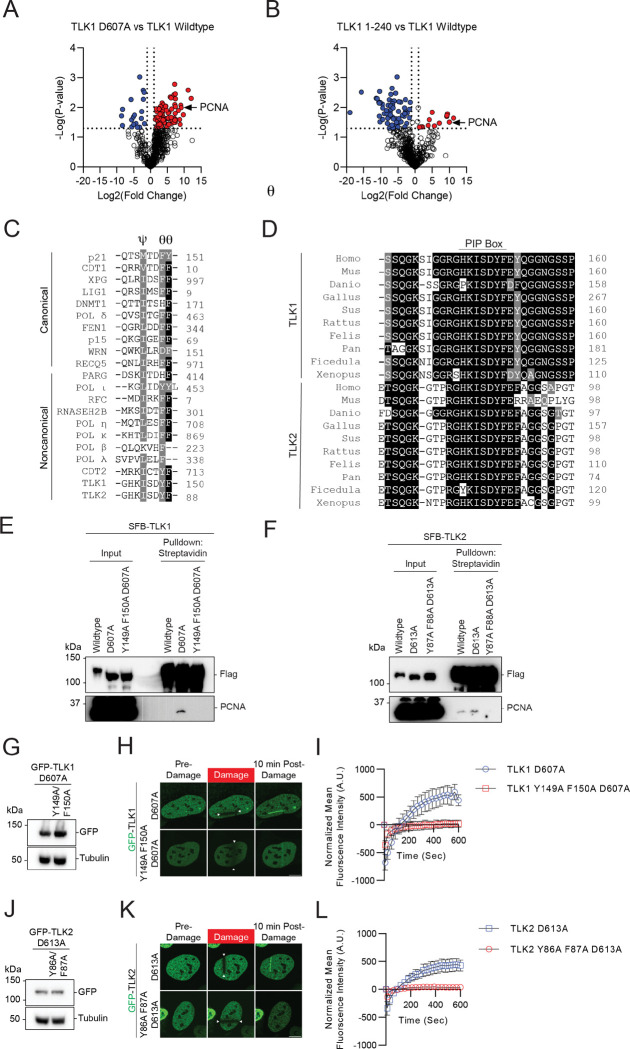
Figure 6. PCNA regulates TLK1 and TLK2 DNA damage recruitment via interaction with their PIP-box.
(A-B) Volcano plot of proteomic analyses between TLK1 wildtype and catalytic mutant D607A or N-terminal fragment a.a. 1–240. Data was analyzed using Perseus and represents technical duplicate data.
(C) Sequence alignment of the canonical and non-canonical PIP-box between TLK, TLK2, and other PCNA interacting proteins. PIP-box QxxϕxxΨΨ, where x represents any amino acid, ϕ represents hydrophobic residues, and Ψ represents aromatic residues) or non-canonical sequences (xxxϕxxΨΨ).
(D) Sequence alignment of the TLK1 and TLK2 PIP-box across species.
(E-F) TLK1 and TLK2 interact with PCNA. HEK293T cells transfected with SFB-TLK1 wildtype, D607A, or PIP box mutant Y149A F150A D607A. Cells were pulled down by streptavidin beads and analyzed by western blot using indicated antibodies.
(G-I) TLK1 PIP box is required for DNA damage recruitment. G. GFP-TLK1D607A and D607A PCNA binding defective mutant (Y149A/F150A) protein expression. H. Representative images of indicated mutants at 10 mins after laser-induced micro-irradiation. The irradiated area is induced by the arrows. I. DNA damage recruitment kinetics quantification as in H. N = 10 cells.
(J-L) TLK2 PIP box is required for DNA damage recruitment. J. GFP-TLK2D613A and D613A PCNA binding defective mutant (Y86A/F87A) protein expression. K. Representative images of indicated mutants at 10 mins after laser-induced micro-irradiation. The irradiated area is induced by the arrows. L. DNA damage recruitment kinetics quantification as in K. n≥10.