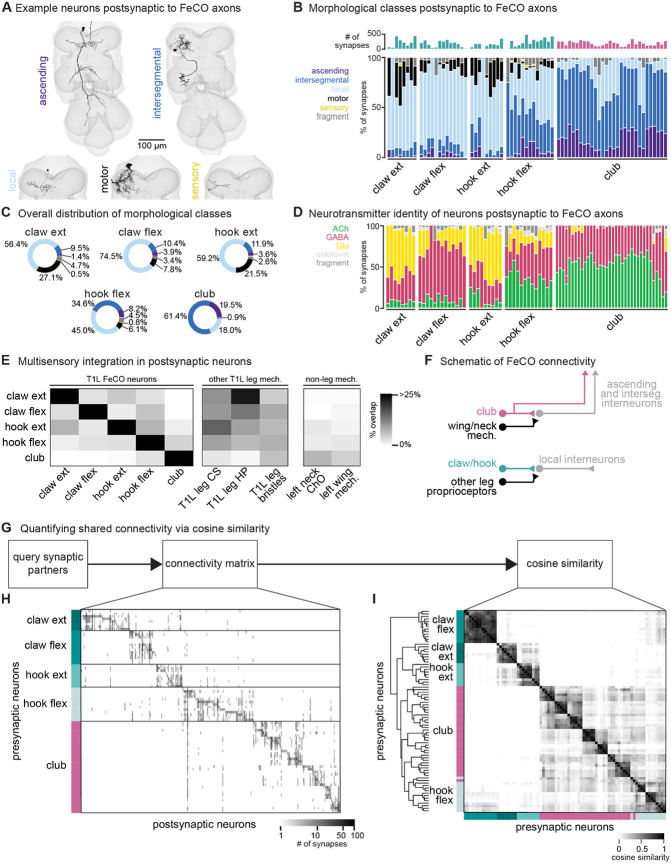
Figure 2. FeCO neurons exhibit subtype-specific postsynaptic connectivity.
(A) We reconstructed all VNC neurons postsynaptic to FeCO axons from the front left leg (T1L) and classified them into morphological classes. Example provided from each class. (B) Percent of synapses from each FeCO axon that are made onto VNC neurons of each morphological class. Top bar plot shows the total number of output synapses made by each FeCO axon. (C) Per FeCO subtype, the total fraction of output synapses made onto each morphological class. (D) Proportion of total synapses made by each FeCO neuron onto cholinergic (green), glutamatergic (yellow), GABAergic (pink), and unidentified (light gray) hemilineages. (E) Heatmap shows the percent of neurons postsynaptic to a particular T1L FeCO subtype (as indicated along the rows) that also receive synaptic input from an alternate somatosensory population: T1L FeCO neurons, including claw extension axons, claw flexion axons, hook extension axons, hook flexion axons, or club axons, other T1L leg mechanosensory neurons, including campaniform sensilla axons (CS), hair plate axons (HP), or bristle axons, and non-leg somatosensory neurons, including left neck chordotonal organ axons or left wing somatosensory axons. We found that neurons postsynaptic to claw and hook axons also integrate information from other leg proprioceptors such as HP axons and CS axons. In contrast, neurons postsynaptic to club axons do not integrate information from other leg proprioceptors, but they do integrate information from wing and neck somatosensory axons. (F) Schematic of FeCO connectivity. Club information is conveyed primarily to ascending and intersegmental neurons, who also receive information from wing and neck somatosensory neurons. Information from claw and hook axons is primarily relayed to local interneurons, which also receive information from other leg proprioceptive neurons. (G) By querying the connectivity of each postsynaptic partner of each reconstructed FeCO neuron, we obtained H) a connectivity matrix and I) a cosine similarity matrix. (H) Connectivity matrix between FeCO axons and postsynaptic VNC neurons. The shading of each tick indicates the number of synapses from each FeCO axon (row) onto each postsynaptic VNC neuron (column). Colored bars along the left indicate the presynaptic FeCO subtype for that row. FeCO axons are organized by morphological subtype and then by their cosine similarity scores. VNC neurons are organized by their cosine similarity scores. (I) Clustered pairwise cosine similarity matrices of all FeCO axons based on their postsynaptic connectivity. The cosine similarity between two neurons is the dot product of the normalized (unit) column weight vectors. If two FeCO neurons synapse with similar synaptic weights onto the same postsynaptic neuron, relative to the FeCO’s total output, the pairwise cosine similarity is 1. FeCO neurons with similar postsynaptic connectivity patterns cluster together, forming connectivity clusters.