Figure 6. Vibration signals from club neurons are transmitted directly and indirectly to the brain and integrated with mechanosensory signals from the antenna.
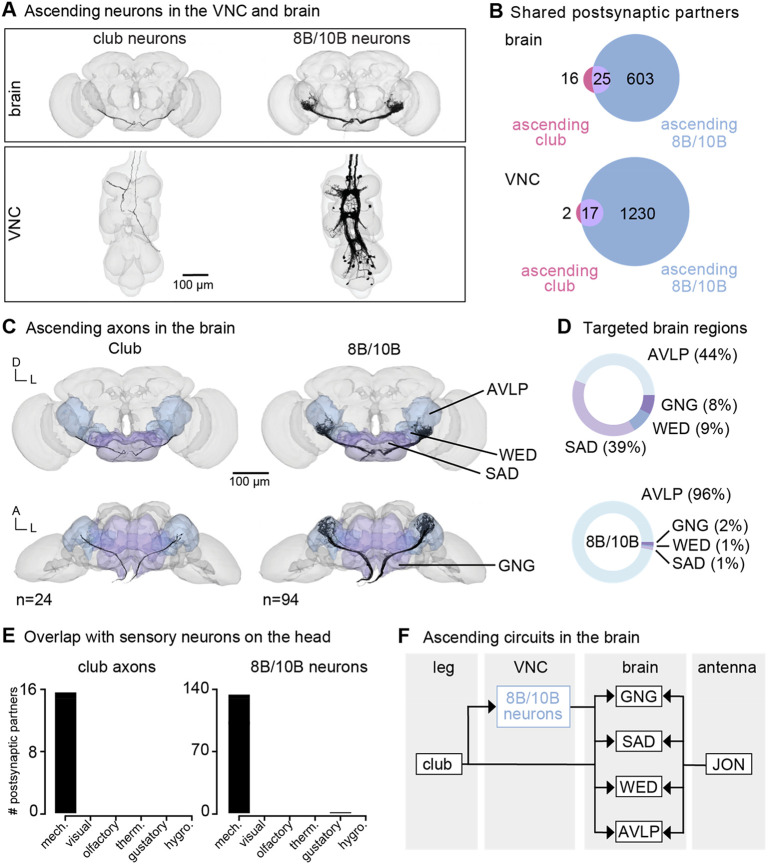
(A) Ascending club axons and ascending 8B and 10B interneurons that are reconstructed in the FANC (bottom, 8 club axons and 52 interneurons) and Flywire (top, 24 sensory axons and 94 interneuron axons) datasets. (B) Venn diagrams of shared postsynaptic partners between ascending club neurons and ascending 8B/10B neurons in the VNC (top) and brain (bottom). (C) Images of the ascending club axons (n = 24) and ascending 8B and 10B interneurons (n = 94) in the brain dataset with targeted brain regions highlighted (Flywire). Axons project to the anterior ventrolateral protocerebrum (AVLP), wedge (WED), saddle (SAD), and gnathal ganglion (GNG). (D) Percentage of synaptic outputs from ascending club axons (top) and ascending 8B/10Bs interneurons (bottom) in each brain region. The ascending club axons and ascending interneurons differ with respect to distribution of output synapse location. (E) Number of postsynaptic partners of ascending club axons (left) and ascending 8Bs/10Bs (right) that are shared with other sensory neurons in the brain. (F) Circuit diagram depicting the projection patterns of ascending club and ascending 8B/10B interneurons in the brain, which integrate with antennal mechanosensory circuits.