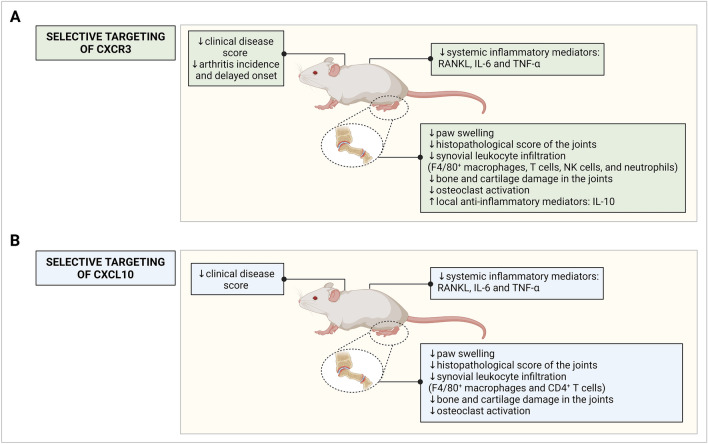
Fig. 3.
Schematic representation of the effects of targeting the IFN-inducible CXCR3 chemokine network on arthritis symptoms in rodent models. Symptomatology, cellular and molecular outcomes are depicted for rodent models undergoing therapies or depletions targeting A CXCR3 and B CXCL10. Selective targeting of CXCR3 was established through genetic ablation, CXCR3 antagonists (AMG 487, TAK-779, SCH 546,738, or JN-2) or CXCR3-targeting monoclonal antibodies. Selective targeting of CXCL10 was realized through genetic ablation, a CXCL10-encoding DNA vaccine, CXCL10-targeting monoclonal antibodies, a CXCL10-encoding retrovirus or a bispecific antibody targeting CXCL10 and TNF-α. CXCL, CXC chemokine receptor ligand, CXCR CXC chemokine receptor, IFN interferon, IL interleukin, NK natural killer, RANKL Receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa-Β ligand, TNF-α tumor necrosis factor α