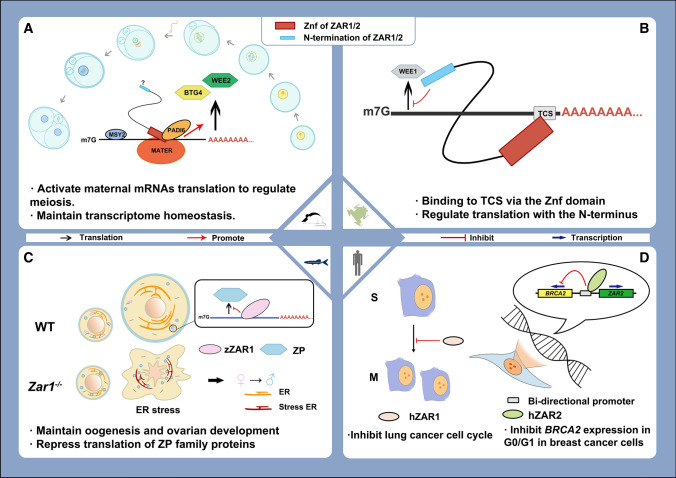
Fig. 4.
Function model of Zar1/2 among species. The function of Zar1/2 among species reported to date. A In Mus musculus, ZAR proteins were reported to activate translation and maintain homeostasis of the maternal transcriptome by binding to mRNAs and interacting with other proteins, such as MSY2 and PADI6, in oocytes with partially functional complementarity. The C-terminus is functionally involved in the binding of RNAs and proteins. B In Xenopus laevis oocytes, ZAR proteins were reported to specifically recognize the TCS in the 3ʹ UTR of Wee1 mRNA, which represses translation. C In zebrafish, ZAR1 was reported to bind mRNAs of zona pellucida (Zp) and repress their translation in early stage oocytes. Deletion of ZAR1 induces endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress, which leads to oocyte apoptosis and female-to-male sex transition. zZAR1 refers to ZAR1 in zebrafish. D In humans, ZAR1 and ZAR2 were found to function in repressing the development of cancer cells, whereby ZAR1 represses cell cycles and causes lung cancer cells to arrest at the S phase. ZAR2 binds to the bi-promoter of BRCA2 and ZAR2, thereby repressing the transcription of BRCA2 to repress breast cancer cells. hZAR1 and hZAR2 refer to ZAR1 and ZAR2 in humans, respectively