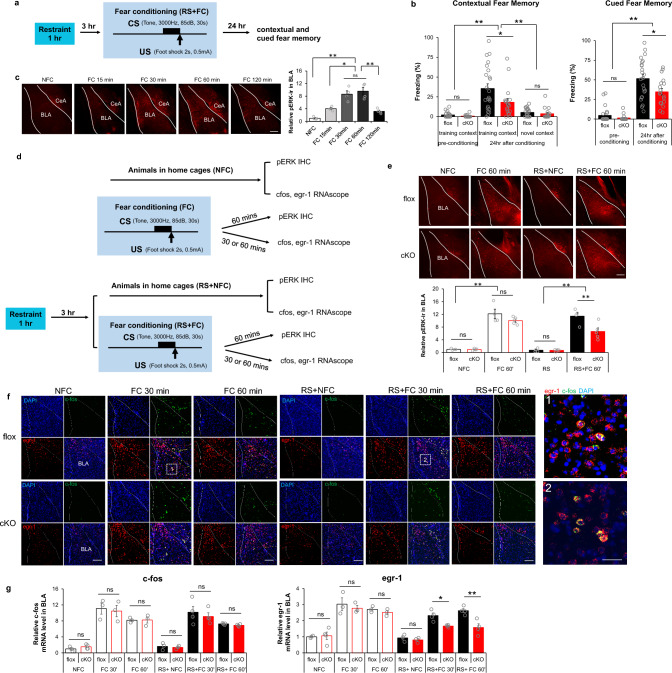
Fig. 5.
Differential dependency of RapGEF2 in immediate early gene activation in basolateral amygdala after fear conditioning with prior restraint stress. a and b Both contextual and cued fear memory was impaired in Camk2α-cre+/-::RapGEF2fl/fl mice (cKO) when 1 h restraint stress was applied 3 h prior to fear conditioning. Scheme of fear conditioning test employed is shown (a). cKO mice showed impaired contextual memory to the training context, not to a novel context, 24 h after conditioning, compared to controls (b, left panel). cKO mice showed attenuation in freezing during the tone presentation in a non-training context when memory was retrieved 24 h after conditioning (b, right panel). Two-way ANOVA followed by post hoc Bonferroni t-test, **p < 0.001, *p < 0.05. N = 23 flox mice, N = 18 cKO mice. c ERK activation in BLA after fear conditioning. pERK immunoreactivity (ir) in amygdala of RapGEF2fl/fl mice sacrificed at 15, 30, 60 min or 120 min after fear conditioning (FC15 min, FC 30 min, FC 60 min or FC 120 min) or from mice that stayed in home cage (NFC). Phospho-ERK IR in the BLA at different time points after fear conditioning was quantified using ImageJ, showing most prominent activation in BLA occurring 30–60 min after fear conditioning. N = 4 for animal number in each group. One-way ANOVA followed by post hoc Bonferroni t-test, *p < 0.05; **p < 0.001. Scale bar: 200 µm. d Experimental procedure to examine phospho-ERK and IEGs activation in BLA after fear conditioning without or with restraint stress. e ERK activation in the BLA of cKO mice 1 h after fear conditioning was not significantly different from that of flox mice. However, phospho-ERK IR level in the BLA was attenuated in cKO mice when acute restraint stress was applied prior to fear conditioning. N = 4 ~ 5 for animal number in each group. Two-way ANOVA followed by post hoc Bonferroni t-test, **p < 0.001. Scale bar: 200 µm. f Representative RNAscope images of cfos (green) and egr-1 (red) in basolateral amygdala of flox and cKO mice that were sacrificed 30 min or 1 h after fear conditioning with or without restraint stress. Scale bar: 200 µm (left panel), 50 µm (right panel). Upregulation of c-fos mRNA in BLA following fear conditioning occurred exclusively in the neurons with upregulation of egr-1 mRNA. Quantification of c-fos and egr-1 mRNA in BLA of flox mice 30 min after fear conditioning with or without restraint stress revealed that 12.62% ± 0.16% or 16.92 ± 2.70% of egr-1 positive neurons, respectively, are c-fos positive in BLA, N = 3 ~ 4 mice in each group. g cKO mice with RapGEF2 ablation in BLA showed attenuation in egr-1 mRNA, but not in c-fos mRNA increase in BLA after fear conditioning when acute restraint stress was applied prior to fear conditioning. Upregulation of c-fos mRNA in BLA following fear conditioning occurred only in the neurons with upregulation of egr-1 mRNA. C-fos and egr-1 mRNA signals were quantified by NIH Image J using the mean gray values of integrated density after being converted to gray scale; then normalized to average value from flox mice in the home cage (NFC) to obtain “Relative c-fos mRNA level” or “Relative egr-1 mRNA level”. N = 3 ~ 4 for animal number in each group. Two-way ANOVA followed by post hoc Bonferroni t-test, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.001