Fig. 1.
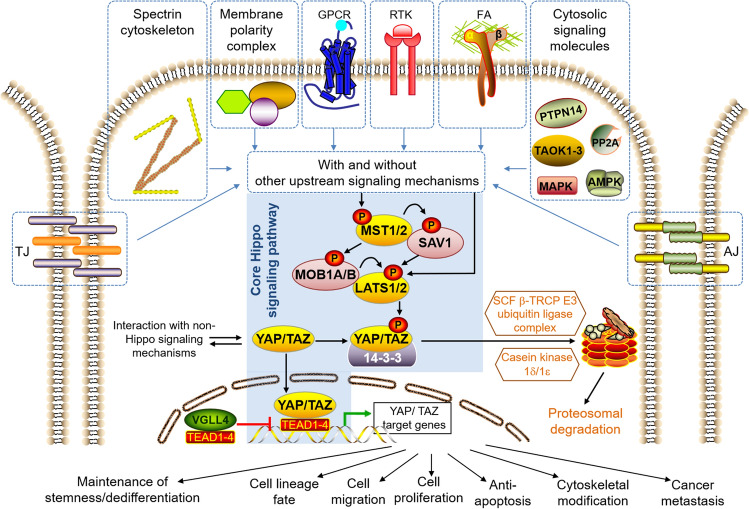
The core of the canonical Hippo signaling pathway is a kinase cascade that in mammals comprises the MST1/2 complex (MST1 & MST2, also known as STK4 & STK3, respectively), LATS1/2 complex (LATS1 & LATS2, large tumour supressor kinase 1 & 2, respectively), the adaptor proteins: SAV1 (Salvador 1), MOB1A and MOB1B, the transcriptional co-activators YAP/TAZ, the 14-3-3 protein that binds only to phosphorylated YAP/TAZ, and finally the TEAD transcription factors (TEAD1–TEAD4) that activate the transcription of specific genes upon binding to unphosphorylated YAP/TAZ. The Hippo signaling pathway can be initiated upon phosphorylation of MST1/2 or LATS1/2 by various upstream signaling mechanisms that may involve Focal adhesions (FAs), G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs), Receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs), Adherens junctions (AJs), Tight junctions (TJs), Spectrin cytoskeleton, Membrane polarity complexes (i.e. Crumbs, Scribble, aPKC-PAR) and various cytosolic signaling molecules (i.e. PP2A, TAOK1/2/3, MAPK, AMPK, and PTPN14). The activated MST1/2 complex phosphorylates the adaptor proteins SAV1, MOB1A and MOB1B, which in turn assist the MST1/2 complex in recruiting, phosphorylating and activating the LATS1/2 complex. Nevertheless, it must be noted that the LATS1/2 complex is not necessarily activated only by the MST1/2 complex, but can also be phosphorylated and activated by other upstream signaling mechanisms. Upon activation, the LATS1/2 complex phosphorylates YAP/TAZ, which then binds to the 14-3-3 protein. This in turn prevents the phosphorylated YAP/TAZ from being translocated into the cell nuclei, and it is then targeted for proteasomal degradation through further phosphorylation by casein kinase 1δ/1ε and ubiquitination by the SCF β-TRCP E3 ubiquitin ligase. By contrast, when MST1/2 and LATS1/2 are not activated, the unphosphorylated YAP/TAZ remains active and is translocated to the cell nuclei where it binds TEAD transcription factors (TEAD1 to TEAD4) to activate the transcription of specific output genes, which may be involved in cell lineage fate, cell proliferation, cell migration, anti-apoptosis, cancer metastasis, cytoskeletal modification, ‘stemness’ maintenance and dedifferentiation. VGLL4 acts as a competitive inhibitor of YAP/TAZ binding to TEAD, resulting in repression of target gene expression