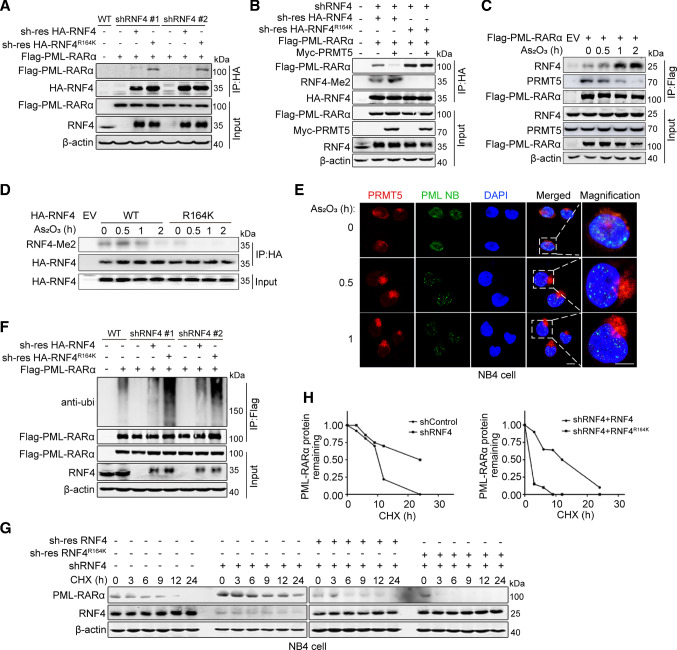
Fig. 5.
RNF4 methylation inhibits PML-RARα ubiquitination and degradation by blocking RNF4–PML-RARα interaction. A The interaction between PML-RARα and RNF4 WT/R164K was examined by co-IP assay in shRNF4 HEK293T cells transfected with shRNA-resistant RNF4 WT or RNF4 R164K mutant plasmids. B The effect of RNF4 methylation on RNF4–PML-RARα interaction was examined by co-IP assay in shRNF4 HEK293T cells transfected with shRNA-resistant RNF4 WT or R164K with/without Myc-PRMT5 plasmids. C The effects of As2O3 on the PRMT5–PML-RARα and RNF4–PML-RARα interactions were analyzed by immunoblotting. HEK293T cells were transfected with the indicated plasmids and treated with As2O3 (1 μM) for 0 h, 0.5 h, 1 h or 2 h. D Immunoblotting to measure the level of RNF4 methylation. HEK293T cells transfected with the indicated plasmids were treated with As2O3 (1 μM) for 0 h, 0.5 h, 1 h or 2 h. E Representative images of NB4 cells immunostained for PML (green), PRMT5 (red) and DAPI (blue). NB4 cells were treated with As2O3 (2 μM) for 0, 0.5 or 1.0 h to examine changes in the co-localization of PRMT5 and PML nuclear bodies. Scale bar, 10 μm. F Denatured IP assays of PML-RARα ubiquitination in shRNF4 HEK293T cells transfected with shRNA-resistant RNF4 WT or RNF4 R164K mutant plasmids. G Immunoblotting to measure the abundance of PML-RARα. The shRNF4 NB4 cells were infected with lentiviruses stably expressing shRNA-resistant RNF4 WT or the RNF4 R164K mutant, after which they were treated with CHX (10 μg/mL). H Semi-quantification of PML-RARα levels, with β-actin used as a loading control. The relative PML-RARα level at time 0 was set as 1