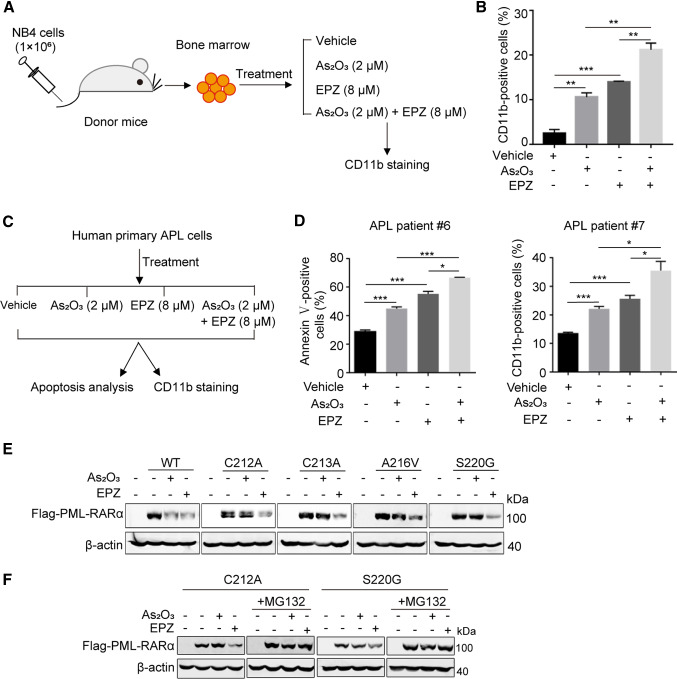
Fig. 7.
The combination of PRMT5 inhibitor EPZ015666 with As2O3 impedes proliferation and differentiation of APL cells. A Experimental design for studying differentiation of BM from APL mice in vitro with the indicated treatment. B The proportion of differentiated cells was determined by flow cytometry. C The strategy for studying apoptosis and differentiation of human primary APL cells from APL patients with the indicated treatment. D The proportions of apoptotic cells (left) and differentiated cells (right) in primary human APL cells (APL patients #6 and #7) were determined by flow cytometry. The results of B and D are shown as the mean ± SEM (n = 3). Statistical analysis was performed using Student’s t test, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. E EPZ induced degradation of PML-RARα in cells that were resistant to As2O3. HeLa cells transfected with the indicated plasmids were treated with As2O3 (1 μM, 16 h) or EPZ (5 μM, 60 h) and the protein abundance of PML-RARα was detected by western blotting. F Determination of the PML-RARα protein degradation pathway by EPZ. HeLa cells transfected with the indicated plasmids were treated with As2O3 (1 μM, 16 h) or EPZ (10 μM, 20 h), and 10 μM MG132 was added to culture for an additional 12 h, after which, the abundance of PML-RARα protein was determined by western blotting