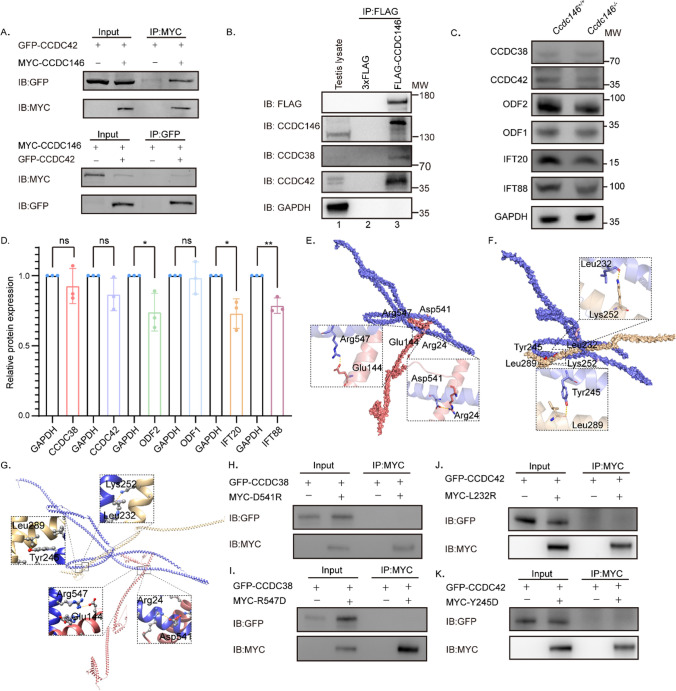
Fig. 6.
CCDC146 interacts with CCDC38 and CCDC42. A CCDC146 interacted with CCDC42. pCSII-MYC-Ccdc146 were transfected into HEK293T cells with pEGFP-C1-Ccdc42 48 hours after transfection; cells were collected for immunoprecipitation with anti-MYC, and detected by anti-GFP or anti-MYC antibodies, respectively. B CCDC146 interacted with CCDC38 and CCDC42 in testis. Co-IP of CCDC38 and CCDC42 with FLAG-CCDC146 from testis lysate using anti-FLAG magnetic beads, followed by western blotting with anti-CCDC38, anti-CCDC42, anti-CCDC146 and anti-FLAG (CCDC146) antibodies. C, D Western blots showing CCDC38, CCDC42, ODF2, IFT88, IFT20, and ODF1 protein levels in lysates from Ccdc146+/+ and Ccdc146−/− mice testes. GAPDH served as a loading control. ODF2, IFT88, and IFT20 protein levels were reduced in Ccdc146−/− testes compared with Ccdc146+/+ testes. Data are presented as means ± SEM. two-tailed Student’s t test; ns: no significance; *P < 0·1; **P < 0·01. E Binding mode of CCDC38 on the CCDC146 predicted by docking. Detailed interaction network between CCDC38 and CCDC146. Key residues of CCDC146 (blue) and CCDC38 (light red) are displayed as sticks. H-bonds are displayed in dash lines. F Binding mode of CCDC42 on the CCDC146 predicted by docking. Detailed interaction network between CCDC42 and CCDC146. Key residues of CCDC146 (blue) and CCDC38 (light yellow) are displayed as sticks. H-bonds are displayed in yellow dashed lines. G Alignment of the mode of CCDC38 and CCDC42 on the CCDC146 predicted by docking. H–I Interactions between CCDC38 and WT or D541, or R547 mutants of truncated CCDC146 were detected by Co-IP assays. J–K Co-IP assays detected interactions between CCDC42 and WT or L232, or Y245 mutants of truncated CCDC146