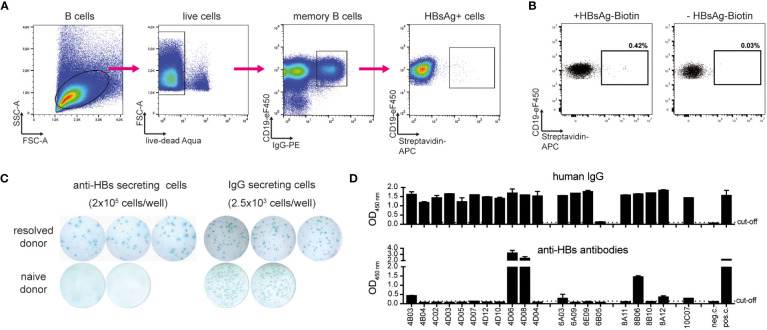
Figure 1.
Identification and isolation of HBV-specific memory B cells. (A) Representative gating strategy to identify and isolate live CD19+ IgG+ HBsAg+ memory B cells of a donor with resolved acute HBV infection after magnetic B-cell enrichment and incubation with HBsAg-biotin. Arrows indicate stepwise gating. (B) HBsAg+ gate of B cells of the donor with resolved acute infection. Comparison to a staining control using streptavidin-APC. Depicted cell populations were pre-gated on live CD19+ IgG+ B cells. Frequencies refer to IgG+ cells. (C) Representative ELISpot well images of HBsAg-specific and total IgG. ELISpot was performed after in vitro stimulation of PBMC for five days. (D) Transfection of HEK293 cells with corresponding antibody heavy and light chain plasmids. Secretion of total IgG (detected with polyclonal goat ant-human IgG HRP) and anti-HBs-specific antibodies (on protein G-coated plates, detected with HBsAg-biotin and Avidin-HRP) was determined via ELISA. Medium only served as negative control (neg. c.). Polyclonal HBIg diluted in medium served as a positive control (pos. c.). Data points represent mean values ± SD from triplicates.