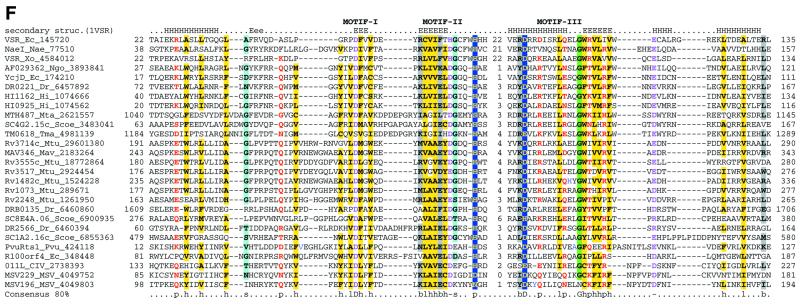
Figure 3.
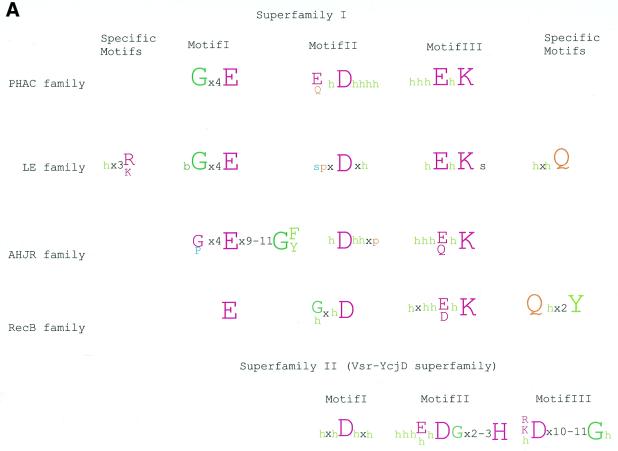
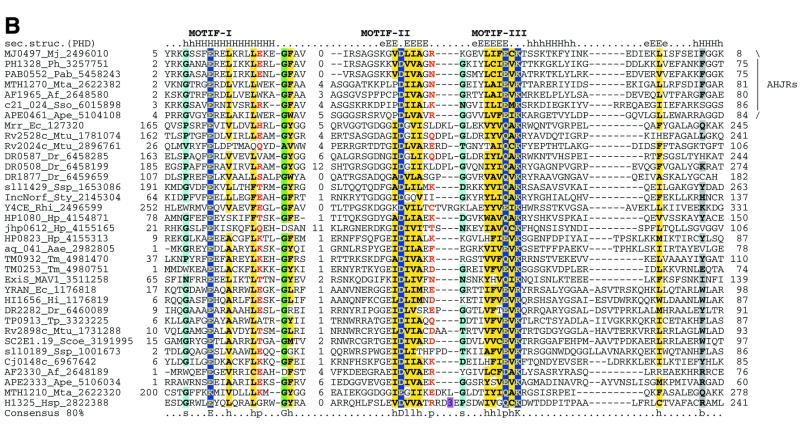
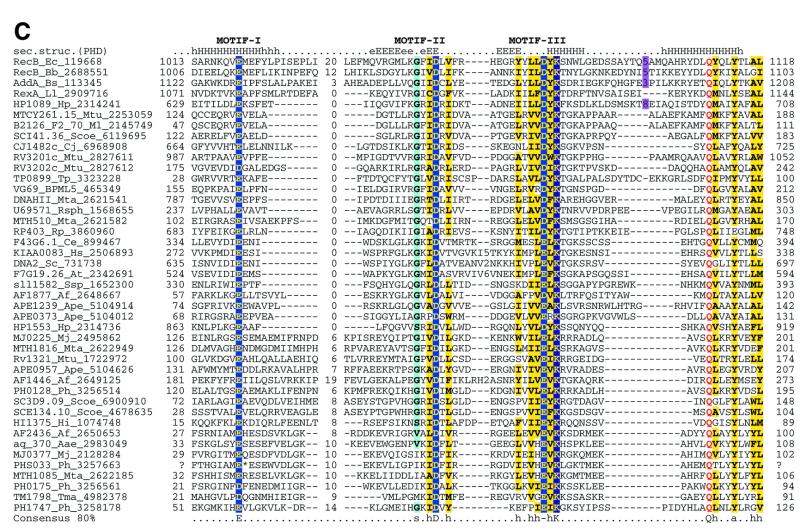
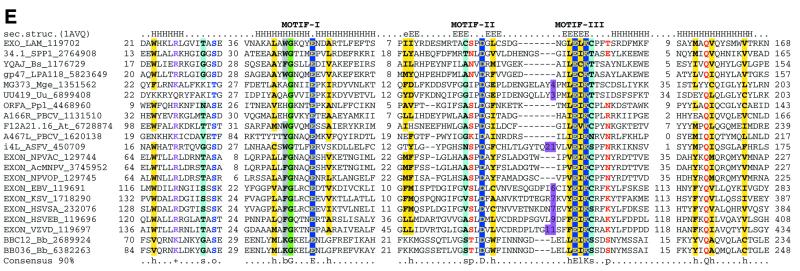
Multiple alignments of the HJRs and related nucleases of the endonuclease fold. (A) A schematic of the conserved motifs containing the (predicted) catalytic residues. (B) Superfamily I: the AHJR–Mrr family. (C) Superfamily I: the RecB family. (D) Superfamily I: the PHAC family. (E) Superfamily I: the λ exonuclease family. (F) Superfamily II: Vsr homologs. The schematic representation in (A) shows the configuration of the three conserved motifs of superfamilies I and II as well as certain family-specific motifs described in the text. The conserved residues that are present in >25% of the cases are shown by the single letter code in upper case. In other cases the general consensus category for the residues as indicated in the legend to Figure 1 is shown in lower case. The alignment notation is as indicated in the legend to Figure 1. The conserved motifs of each superfamily are indicated above the alignment. All families of superfamily I share three conserved motifs as shown in (A), but because of the absence of extended sequence similarity between the families, the alignment for each family is shown separately (B–F). In (E) only two sequences from B.burgdorferi, BB036 from the chromosome and BBC12 from linear plasmid C, are shown; the remaining plasmid-encoded sequences are nearly identical to these. Blue letters in some of the sequences in the alignment indicate anamolous inserts that have been excised. Additional species abbreviations: Sty, Salmonella typhimurium; Rsph, Rhodopseudomonas spheroides; Hs, Homo sapiens; Ll, Lactococcus lactis; Ban, Bacillus anthracis; Tfo, Thiobacillus ferroxidans; Vic, Vibrio cholerae; Coxb, Coxiella burnetti; Rhi, Rhizobium sp.; LPA118, Listeria phage A118; NPVAC, AcMNPV and NPVOP, nuclear polyhedrosis viruses of Autographa califorinica, Bombyx mori and Orgyia pseudotsugata; EBV, Epstein–Barr virus; KSV, Kaposi sarcoma virus; HSVSA, herpes virus saimiri; HSVEB, equine herpes virus B; VZVD, varicella zoster virus D.