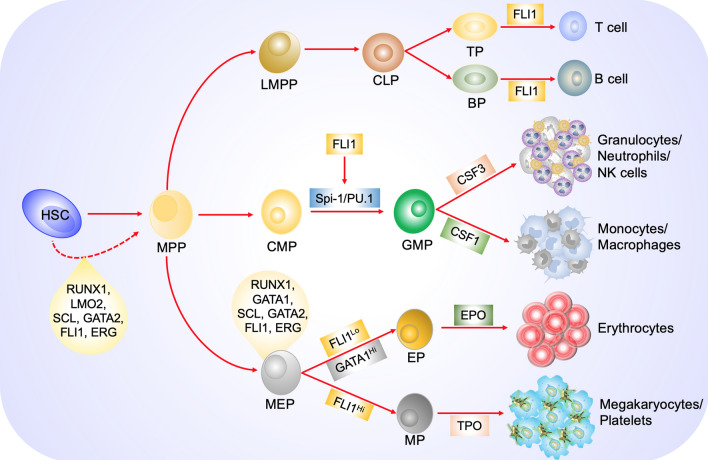
Fig. 4.
The role of FLI1 in hematopoiesis: FLI1, in combination with other transcription factors (TFs), maintains HSC survival, proliferation, and differentiation. In cooperation with these additional TFs, FLI1 expression level (LowLo or HighHi) defines the fate of MEPs to become erythroid or megakaryocytic cells, respectively. Regulation of the ETS gene Spi-1/PU.1 by FLI1 promotes CMP differentiation to monocyte/macrophages or granulocytes/neutrophils. Finally, FLI1 expression plays a critical role in differentiation of lymphoid progenitors toward mature T and B cells. HSC (hematopoietic stem cell), MPP (multi-potential progenitor), MEP (megakaryocyte erythrocyte progenitor), LMPP (lymphoid multi-potential progenitor), CMP (common myeloid progenitor), LMPP (lymphoid primed multi-potential progenitor), CLP (common lymphoid progenitor), GMP (granulocyte monocyte progenitor), EP (erythroid progenitor), MP (megakaryocyte progenitor), BP (B-cell progenitor), TP (T-cell progenitor)