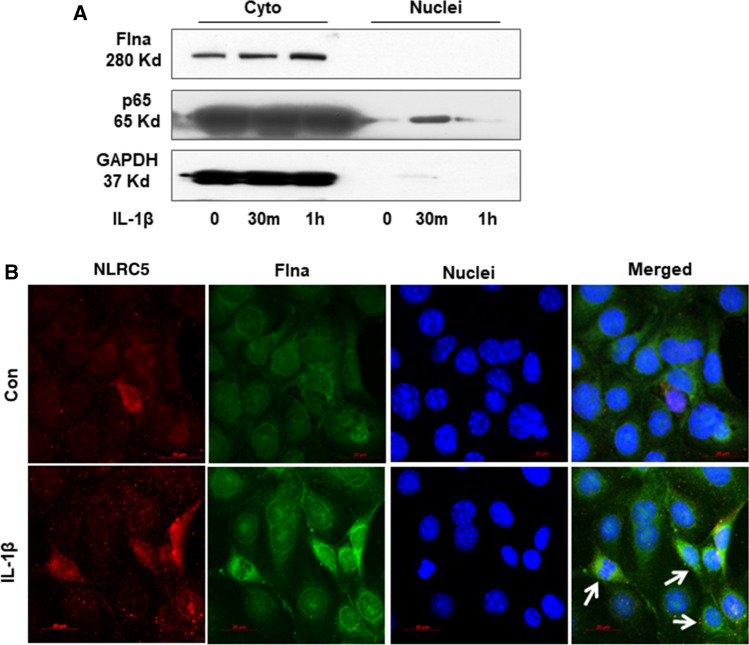
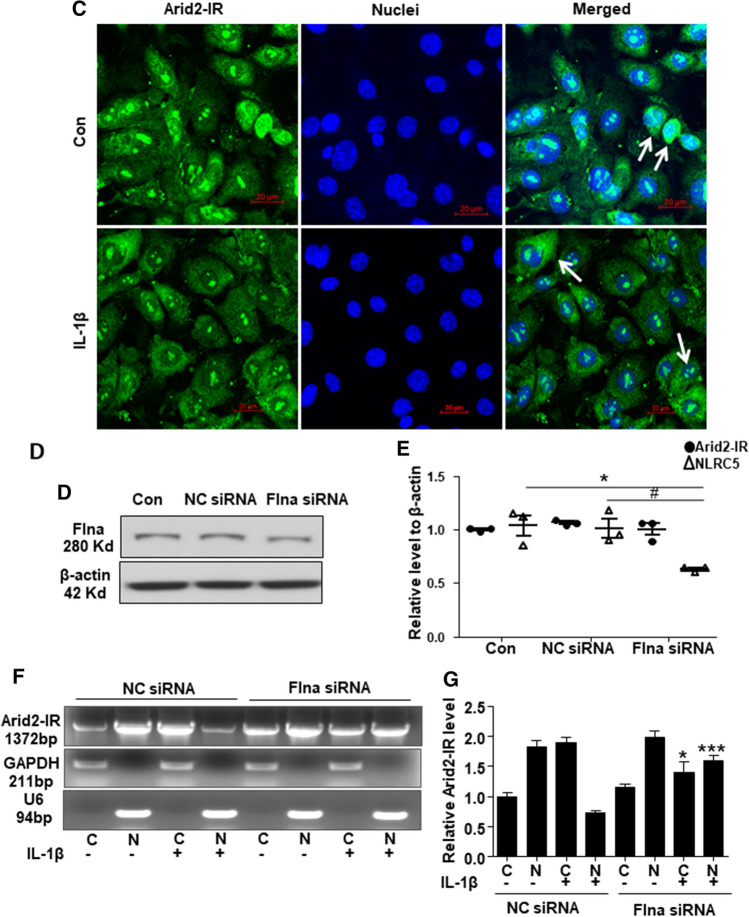
Fig. 7.
a Western bolt was performed to analyze the nuclei and cytoplasm protein in IL-1β (10 ng/mL) treated mTECs at 30 min and 1 h. b Immunofluorescence was performed to detect cellular location of Flna (green) and NLRC5 (red) in mTECs treated with IL-1β (10 ng/mL) for 30 min. White arrows indicated the mTECs that Flna protein was significantly increased in the cytoplasm after IL-1β treatment, which NLRC5 was also up-regulated. c Fluorescence in situ hybridization was performed to detect cellular location of Arid2-IR (green) in mTECs treated with IL-1β (10 ng/mL) for 30 min. White arrows indicated the mTECs which Arid2-IR was recruited to the cytoplasm after IL-1β treatment. d The protein level of Flna was detected in Flna or NC siRNA(200 nM) transfected mTECs by Western bolt. e QPCR presentation of relative level of Arid2-IR and NLRC5 normalized to β-actin in Flna or NC siRNA-transfected mTECs. All data are mean ± SEM of at least three independent experiments. *p < 0.05 versus control, #p < 0.05 versus NC siRNA. f Agarose gel electrophoresis of RT-PCR was used to detect Arid2-IR level in the nuclei and cytoplasm fraction of IL-1β (10 ng/mL) treated mTECs. MTECs were transfected with Flna or NC siRNA (200 nM) for 24 h before IL-1β treatment. C cytoplasm, N Nuclei. g Statistical analysis was used to represent Arid2-IR level in mTECs. *p < 0.05, ***p < 0.001 versus NC siRNA